- E-mail:support@braincase.cn
- Tel:18971216876
Hu Hailan's research group at Zhejiang University School of Medicine published a review article titled "Research Progress and Prospects for the Development and Application of Neuron Activity-Dependent Tools" in the Chinese version of "Science China: Life Sciences"[1], which discusses the principles and methods of various activity-dependent tools. The application was summarized and reviewed. The article mentioned that Guenthner et al. [2] were the first to achieve permanent marking of active neural clusters through targeted recombination in active populations (TRAP). They knocked CreERT2 behind the c-fos and Arc promoters to prepare FosTRAP and ArcTRAP mice respectively, and then combined Cre-dependent mice or viruses carrying the target gene to label active neural clusters within a specific time interval. Allen et al. [3] further developed TRAP 2 mice by knocking the iCreERT2 gene from the 2A link into the back of the complete c-fos gene, successfully solving the expression interference problem in TRAP mice and significantly improving the signal-to-noise of the tool. Compare.
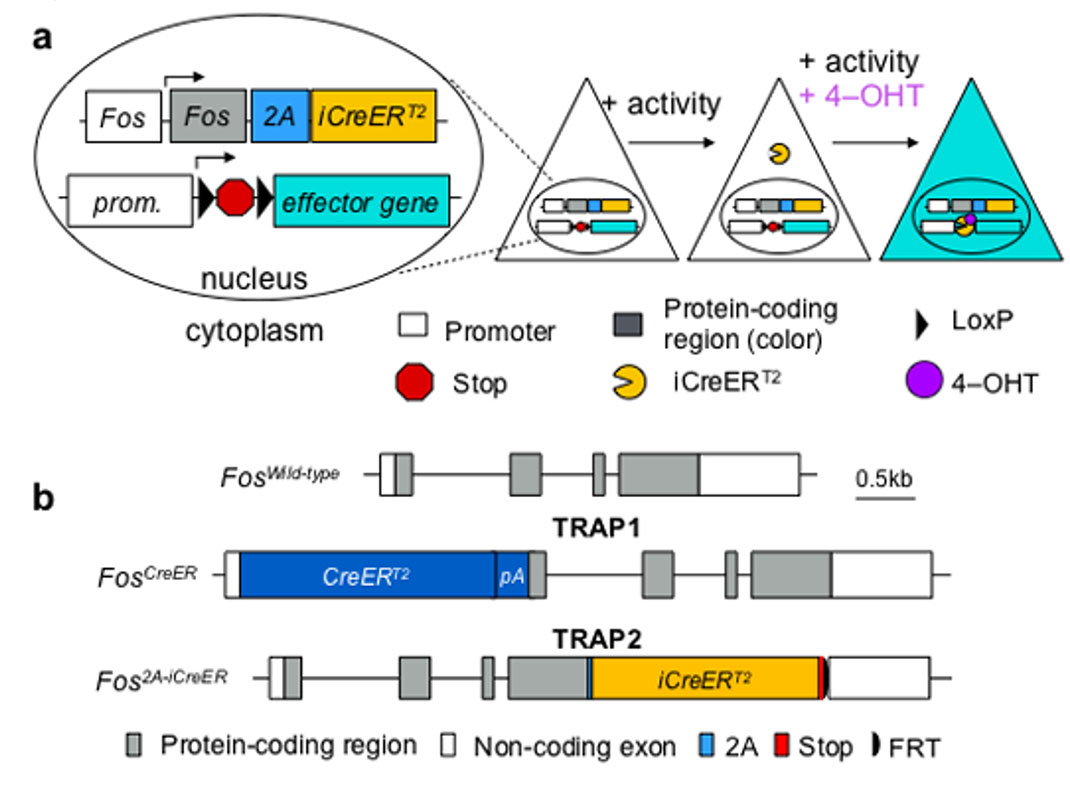
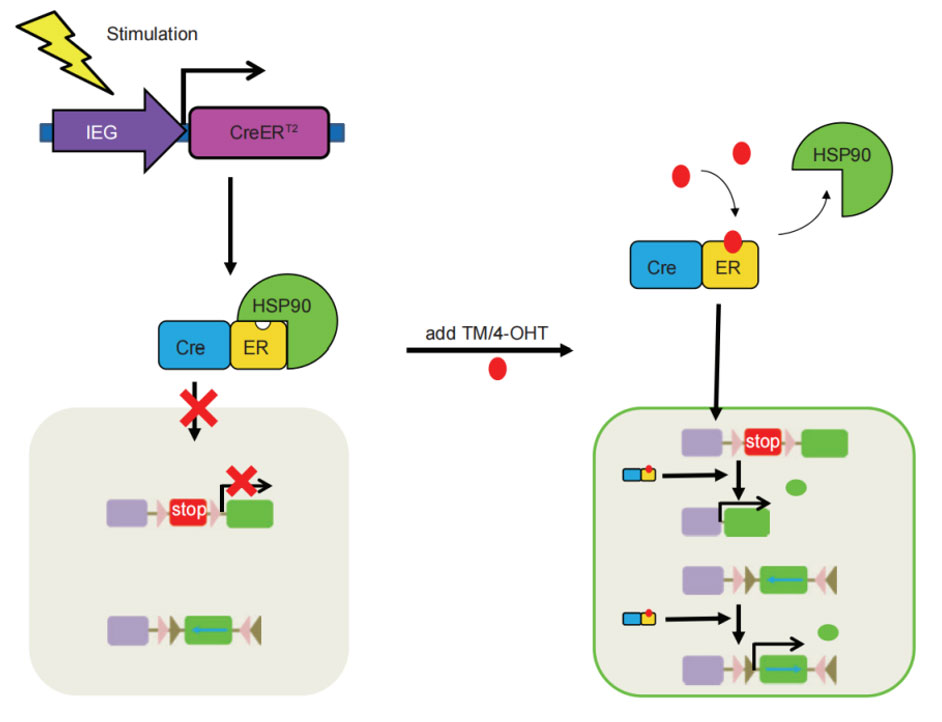
The C-terminus of the Cre element is connected to the ligand-binding domain of the estrogen receptor (ER). Currently, the Cre-ERT2 mutant is the most used. The fusion protein Cre-ERT2 cannot enter the nucleus and is localized in the cytoplasm. After the hormone derivative tamoxifen binds to the Cre-ERT2 receptor binding domain, the protein will dissociate from the anchor protein HSP90 through conformational changes, enter the nucleus, recognize the loxP site, and recombine. By controlling the injection time of tamoxifen, the time specificity of gene recombination can be controlled.
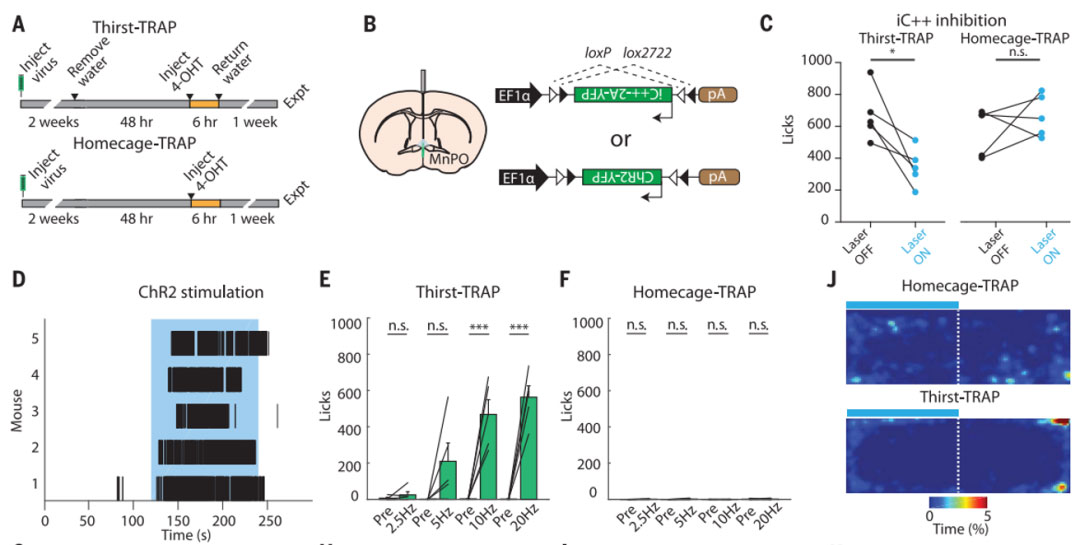
The research team of Luo Liqun and Karl Deisseroth of Stanford University published a research paper titled "Thirst-associated preoptic neurons encode an aversive motivational drive" in the journal Science on September 15, 2017 [3], combining TRAP2 mice with AAV tool viruses The combination method allows the neurons responsible for a certain behavior to be permanently colored under artificial control to achieve optogenetic manipulation of neurons activated within a specific time window. The researchers injected the virus AAV1-EF1a-DIO-ChR2-eYFP or AAV1-EF1a-DIO-iC++-TS-p2A-eYFP into TRAP2 mice in the median preoptic nucleus (MnPO) brain area, and then deprived the mice of the virus for 48 hours. After drinking water, the neurons responsible for thirst in the brains of mice were eventually labeled with optogenetic elements. The results showed that light inhibition can reduce water consumption in water-deprived mice, and light activation can promote water consumption in normal mice. MnPO may be an important link in the brain circuit of thirst, and then the characteristics of its wavelength were used to isolate these colored "thirst neurons". By analyzing the gene transcriptome of neurons isolated from the MnPO, the researchers found that the neurons responsible for thirst in this region are glutamatergic excitatory neurons.
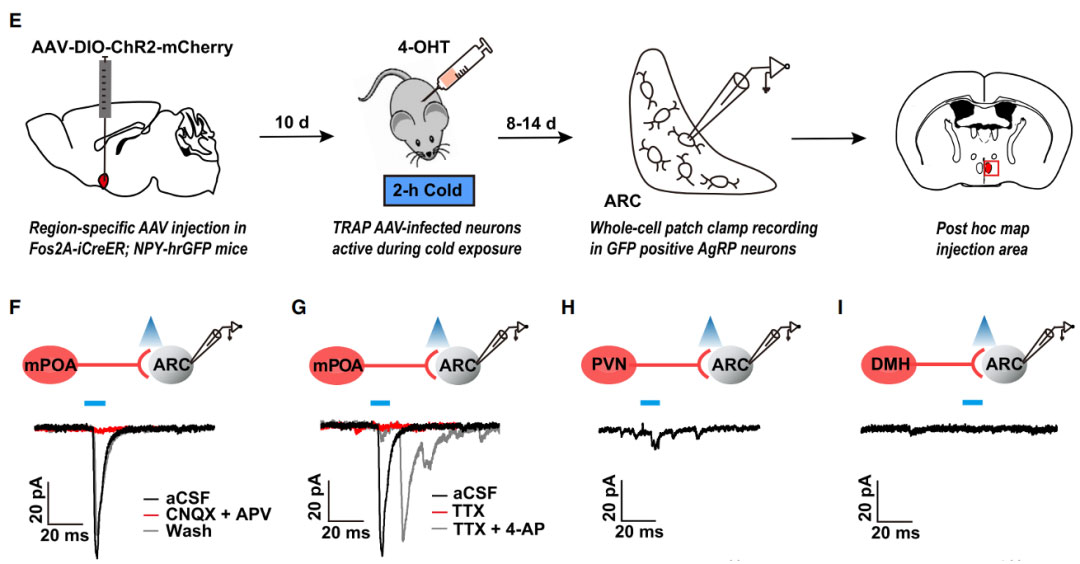
On August 10, 2021, the team of researcher Huang Ju from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine published a new study titled "An mPOA-ARCAgRP pathway modulates cold-evoked eating behavior" in the journal Cell Reports [4]. The researchers found that AgRP neurons are activated in cold environments and functionally verified that the mPOA-ARCAgRP neural pathway is necessary and sufficient for cold-induced eating behavior. In order to verify that the mPOA-ARCAgRP pathway mediates cold-induced feeding behavior, the researchers used TRAP2 mice to inject the virus AAV-DIO-ChR2-mCherry into the mPOA brain region of Fos2A-iCreER mice, and administered 4 doses 10 days after cold exposure. -OHT induces the expression of ChR2, and activating the axonal projection terminals of cold-responsive mPOA neurons to the ARC through optogenetics can significantly increase the number of meals and the time of eating, indicating that activation of the mPOA-ARCAgRP pathway can trigger cold-induced feeding behavior.
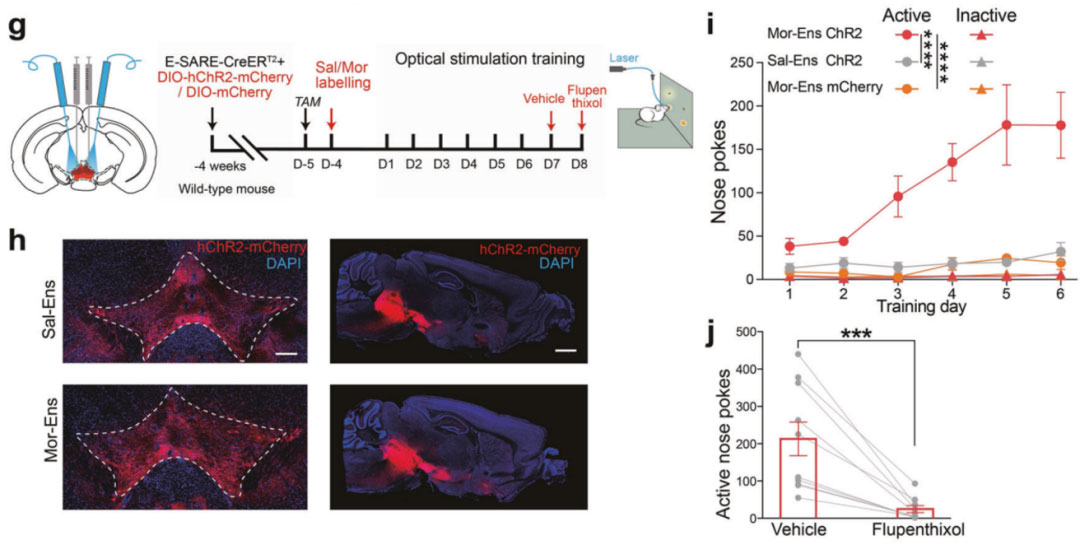
The Ma Lan/Wang Feifei team from the Institute of Brain Science at Fudan University published a research paper titled "CRHCeA→VTA inputs inhibit the positive ensembles to induce negative affect of opiate withdrawal" in Molecular Psychiatry on October 12, 2021 [5]. The researchers used E-SARE (AAV-E-SARE-CreERT2), a functional element that responds to neuronal activity, to mark clusters of neurons activated by morphine's first exposure in the ventral tegmental area (VTA), an important brain area of the mesolimbic system ( Morphine neuron cluster), it was found that the VTA morphine neuron cluster biasedly projects to the nucleus accumbens (NAc) brain region. Researchers injected mixed viruses of AAV-E-SARE-CreERT2 and AAV-DIO-hChR2-mCherry into the VTA area of mice and buried them in optical fibers. After exposure to morphine, they labeled VTA morphine neuron clusters. Light activation can cause the number of nasal touch responses in mice. increased, which can be suppressed by the use of flupentixol (a dopamine antagonist). At the same time, with the help of DA probe, it was found that activating the VTA morphine neuron cluster can promote the release of NAc dopamine. The above results suggest that the VTA morphine neuron cluster preferentially projects to the nucleus accumbens (NAc) brain area. Activating the VTA morphine neuron cluster can promote the release of NAc dopamine, trigger the self-light behavior of mice, and mediate dopamine-dependent Positive reinforcement effect.
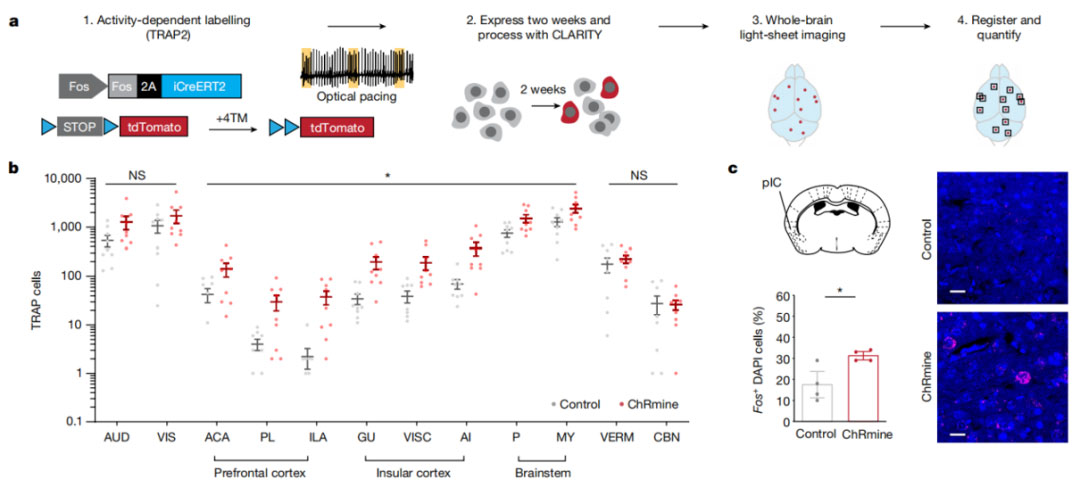
On March 1, 2023, Professor Karl Deisseroth's team at Stanford University published a research paper titled "Cardiogenic control of affective behavioral state" in Nature. This study confirmed that increased heart rate is related to an increase in anxiety-like behavior in mice. The researchers used TRAP2 mice to screen out the brain areas affected by optical pacing. Among them, the posterior insular cortex, an area of the brain responsible for receiving and processing body signals, may mediate the anxiety-like symptoms induced by elevated heart rate. and fearful behavior. Additionally, they found that inhibition of the posterior insular cortex reduced anxiety-like behaviors induced by optically induced increases in heart rate.
[1] Wang Jihua, Hu Hailan. Research progress and prospects for the development and application of neuronal activity-dependent tools [J]. Science China: Life Sciences, 2019, 49 (03): 202-219.
[2] Guenthner CJ, Miyamichi K, Yang HH, Heller HC, Luo L. Permanent genetic access to transiently active neurons via TRAP: targeted recombination in active populations [published correction appears in Neuron. Neuron. 2013;78(5):773 -784.
[3] Allen WE, DeNardo LA, Chen MZ, et al. Thirst-associated preoptic neurons encode an aversive motivational drive. Science. 2017;357(6356):1149-1155.
[4] Yang S, Tan YL, Wu X, et al. An mPOA-ARCAgRP pathway modulates cold-evoked eating behavior. Cell Rep. 2021;36(6):109502.
[5] Jiang C, Yang X, He G, et al. CRHCeA→VTA inputs inhibit the positive ensembles to induce negative effect of opiate withdrawal. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(11):6170-6186.