- E-mail:BD@ebraincase.com
- Tel:+8618971215294
The CRISPR/Cas (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/Cas) system is currently a widely used gene editing technology. Its principle is that the sgRNA produced by CRISPR transcription mediates Cas nuclease to target the target sequence and cut the sequence.
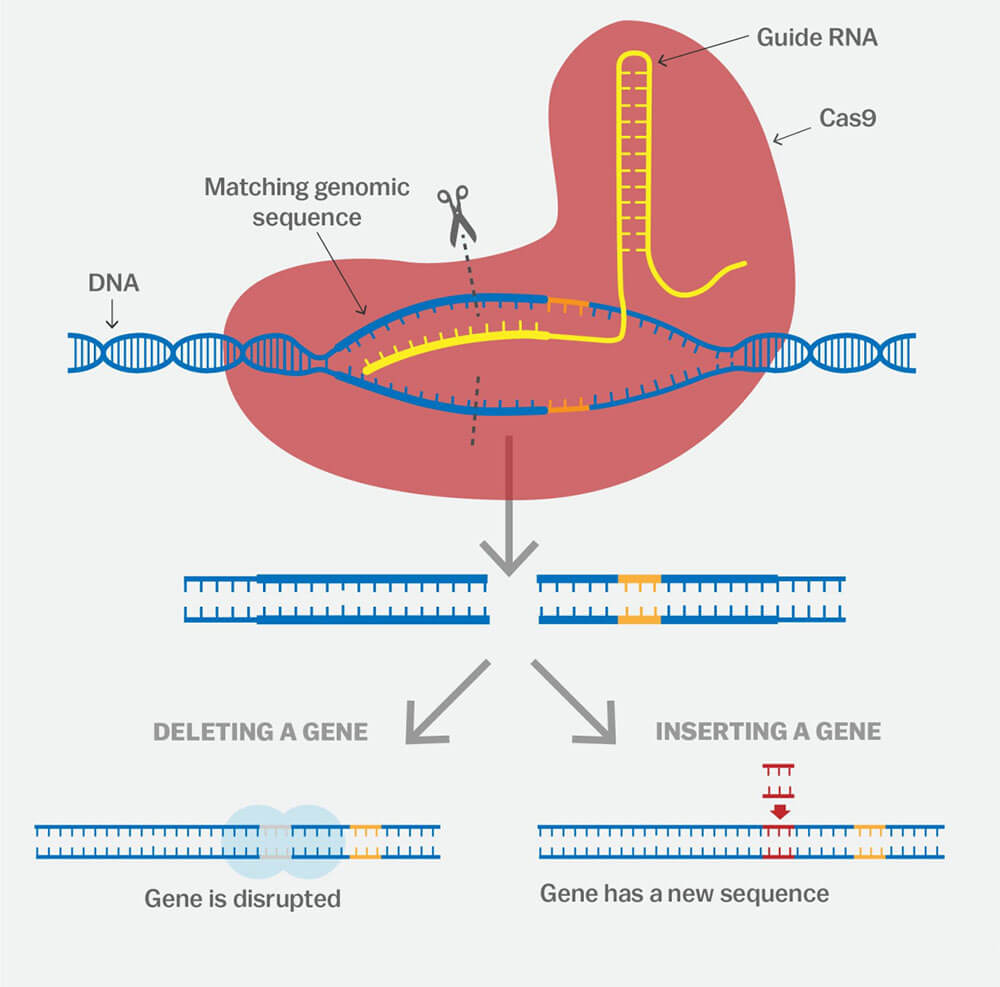
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing (Source: Wellcome Trust SangerInstitute, Sanger)
In the CRISPR/Cas9 system, sgRNA (small guide RNA) recognizes and binds to the target sequence of the target gene, guiding Cas9 to cut at the binding site, resulting in a double-strand break (DSB) in the DNA. The body repairs the DSB through a process called non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). The proteins involved in the repair often insert or delete a few bases at the DNA ends, and the repaired gene loses function due to the mutations introduced, thereby achieving gene knockout in the organism.
Application: establishment of gene knockout cell lines, establishment of gene knockout animal disease models.
Technical advantages: Compared with RNAi, which "knocks down" the target gene at the mRNA level, the CRISPR/Cas9 system causes the deletion of the gene sequence, thereby completely silencing (i.e. knocking out) the target gene.
In the CRISPR/Cas9 system, sgRNA (small guide RNA) recognizes and binds to the target sequence of the target gene, guiding Cas9 to cut the binding site to generate a DNA double-strand break (DSB). Homologous recombination (HR) repair method introduces exogenous donor DNA into the target site of the genome to achieve gene knock-in.
Application: Establishment of gene fragment knock-in cell lines, gene single-base mutation cell lines, and gene knock-in to establish animal disease models.
Technical advantages: simple operation, high efficiency, broad spectrum, and provides BSL-1 and BSL-2 virus injection and experimental operation platforms.
The CRISPR-dCas9 system is a fusion of dCas9 with a transcriptional activator (such as VP64) or a transcriptional repressor (such as KRAB), and then combined with sgRNA can promote or inhibit the expression of the target gene.
Application: Overexpression of target genes in endogenous environment, induction of iPSCs, inhibition of expression, etc.
Technical advantages: simple operation, high efficiency, broad spectrum, and provides BSL-1 and BSL-2 virus injection and experimental operation platforms, and can be combined with RNAi.
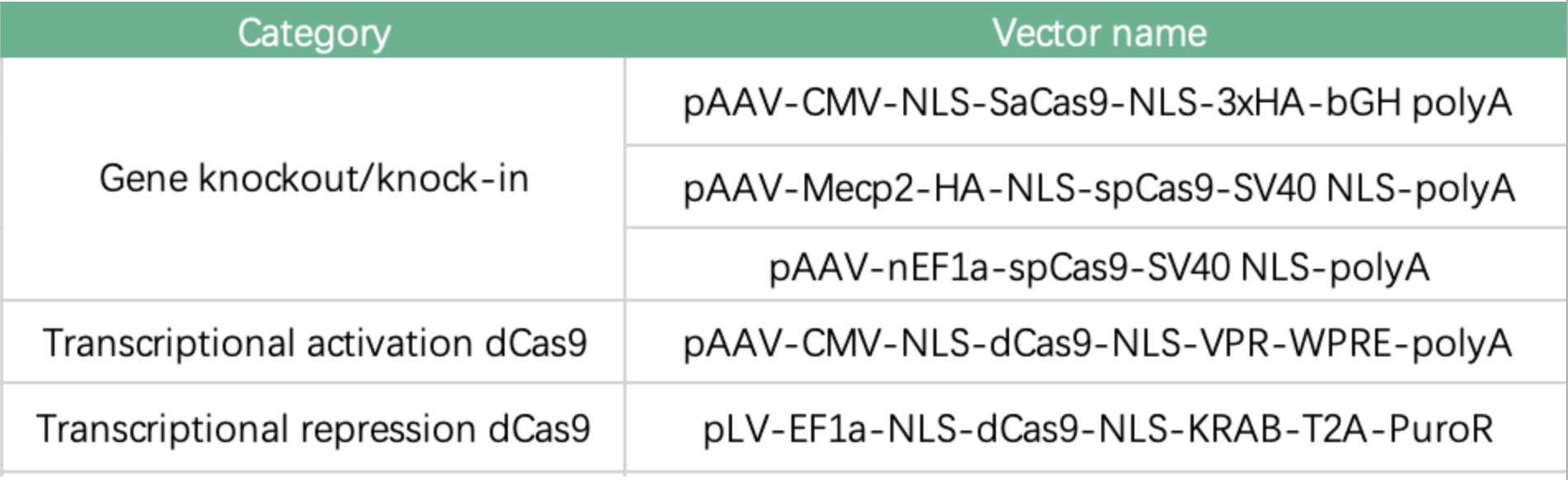
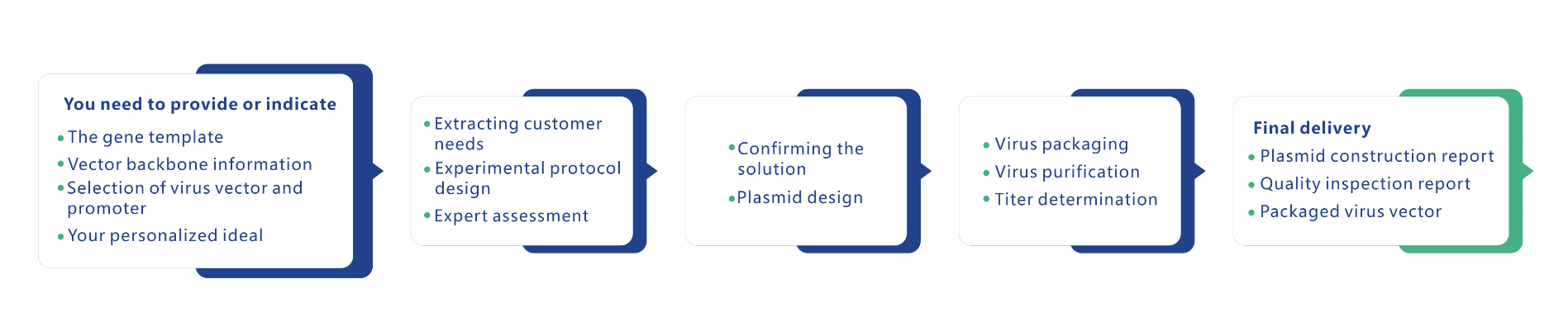
Please download the attchement to know more about service description.
Servicedescription.pdf203.79 KB