- E-mail:bd@braincase.cn
- Tel:+86 18971216876
In addition to the typical neurological disease model, Braincase Biotechnology Co., Ltd. also established other systemic disease model services, mainly including circulatory system, respiratory system, digestive system, urinary system, reproductive system, immune system, ear, nose and throat, ophthalmology, orthopedics and other diseases animal models.
Renal vascular hypertension is caused by the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system caused by ischemia, and the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system has been recognized as the pathogenesis of hypertension. Therefore, animal renal artery stenosis can replicate hypertension models very similarly.
Methods: Healthy male SD rats, weighing 180 ~ 220g, were anaesthetic with pentobarbital sodium. The back was fixed on a wooden board to expose the abdomen, and the median incision of the abdomen was made into the abdominal cavity to separate and expose one renal artery. A silver clip or a silver ring with an inner diameter of 0.2mm was used to narrow the renal artery.
Evaluation: If the postoperative systolic blood pressure is higher than 140mmHg, it is confirmed that the animal model of renal vascular hypertension with two kidneys and one clip type has been successfully established. This model has the advantages of simple modeling, high success rate and strong identity, and is comparable to the pathological process of human hypertension. It is the most commonly used classical animal model of hypertension in the world, and a model widely used in screening antihypertensive drugs at present.
Heart failure is myocardial damage caused by myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, hemodynamic overload, inflammation and other reasons, resulting in changes in myocardial structure and function, and finally lead to poor ventricular pumping or filling function. The main clinical manifestations were dyspnea, fatigue and fluid retention. Chronic heart failure (CHF) refers to a persistent state of heart failure that can be stabilized, worsened, or decompensated. Based on left ventricular ejection fraction, chronic heart failure can be divided into heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (HF-REF) and heart failure with preservation (HF-PEF). Chronic heart failure is a serious and terminal stage of various heart diseases with a high incidence and is one of the most important cardiovascular diseases today.
Methods: Healthy SD rats, weighing 300g, were intraperitoneally injected with doxorubicin hydrochloride solution once a week for 6 weeks.
Evaluation: HE staining showed that the myocardial cells in the normal control group were arranged neatly, with clear structure and compact, and less extracellular interstitium. In the model group, the arrangement of cardiomyocytes was disordered, the cardiomyocytes twisted, hypertrophy, the space between cells increased, the perivascular extracellular stroma increased, and inflammatory cells infiltrated.
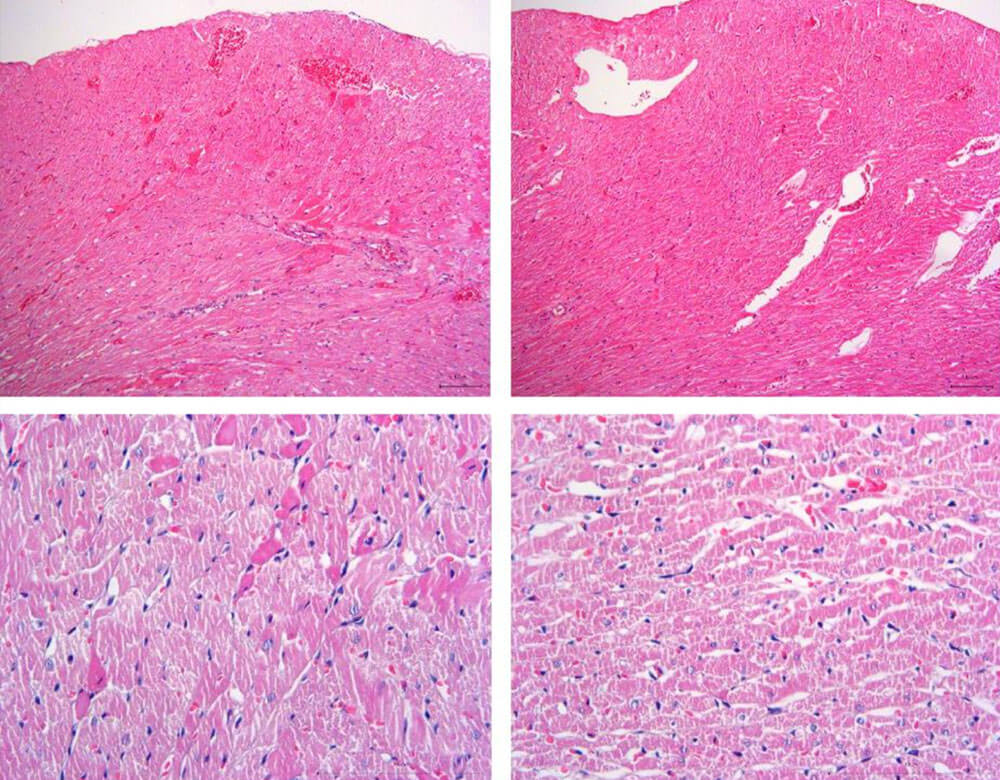
Figure 1. HE staining of heart failure model
Asthma is a chronic airway inflammatory disease characterized by variable airflow obstruction, airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), and airway inflammation. The main clinical symptoms of asthma are shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and increased mucus production after exposure to allergens.
Methods: C57BL/6 mice, 5-6 weeks of age, were intraperitoneally injected with OVA + Al(OH)3 on days 0, 7 and 14; The mice atomized 2% follicle protein for 30 minutes per day from 21 to 25 days.
Evaluation: The number and proportion of eosinophils increased significantly in the model group.
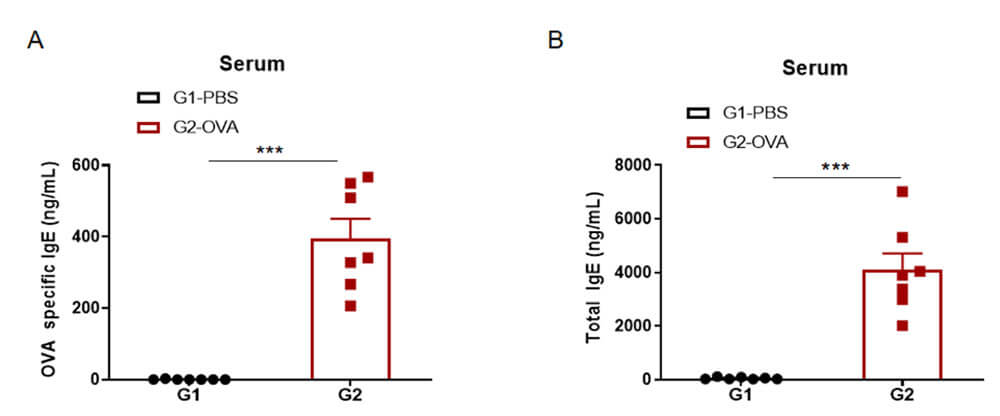
Figure 2 Serum IgE levels in a mouse model of asthma
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive, and fibrotic interstitial pneumonia of unknown origin in adults.
Methods: SPF grade C57/BL6 female mice weighed about 18-20 g. The model was established using bleomycin by endotracheal infusion. Anesthetized mice were fixed on the bench lying on their back, the neck hair was removed and disinfected with alcohol, the skin was cut open, the trachea was exposed layer by layer, and a 1mL syringe was stabbed into the trachea through the space between the two tracheal cartilage rings towards the heart end. Without resistance to withdrawal, bleomycin was injected with 5mg/kg/L (the control group was injected with the same amount of normal saline). Immediately after the operation, the animal was upright and rotated so that the liquid was evenly distributed in the lungs, and the animal was routinely fed after waking up.
2)Evaluation: Intratracheal single administration has the advantages of few administration times, small dose and short molding time, but the animal mortality is high, the operation is complicated, the acute lung injury is severe, the collagen metabolism is mild, the lesion distribution is uneven, and the bronchial area is significant. At present, the animal pulmonary fibrosis induced by one-time intratracheal infusion of bleomycin is the most commonly used and recognized pulmonary fibrosis model at home and abroad.
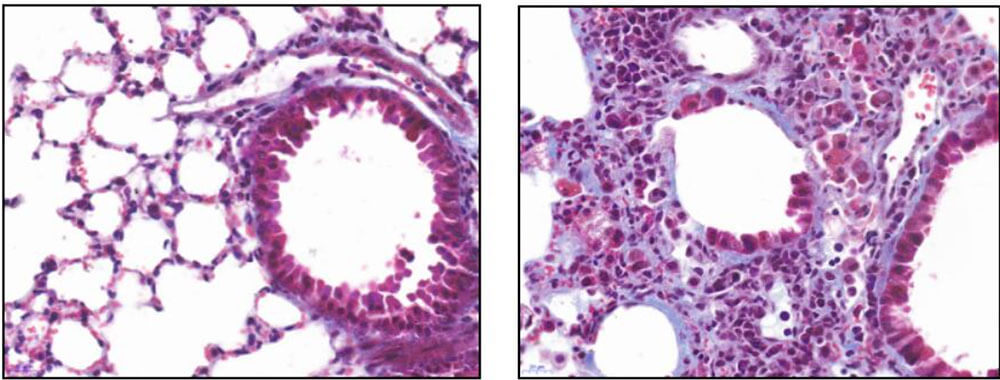
Figure 3. HE staining of pulmonary fibrosis model group
Gastric ulcer is a chronic ulcer that occurs between the pylorus and the cardia of the stomach. It is a common disease in the world. It affects about 10% of the world's population.
Methods: 0.05ml of 100% acetic acid was injected into the anterior wall of gastric antrum after anesthesia. During the injection, the tip of the needle was tilted to ensure that there was a small white spot at the injection site without acetic acid exudation or injection into the stomach cavity. Then, suture the greater omental tissue with 0 silk thread and the serosal tissue of the gastric antrum wall at the injection site. Complete the above steps to put the stomach back in place and suture the abdominal wall. There was obvious gastric ulcer formation 5-10 days after surgery.
Evaluation: The size and depth of gastric antrum ulcer, cleanliness of the base, white moss covering, color, elasticity and hyperemia and edema of the surrounding mucosa were observed.
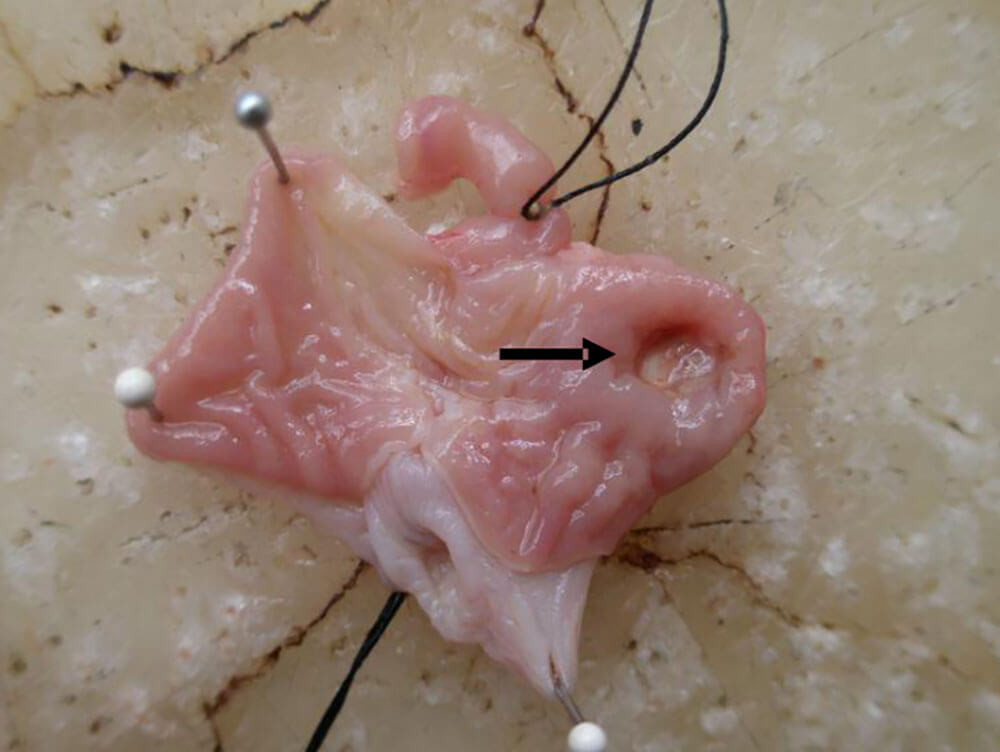
Figure 5. On the fifth day of the acetic acid gastric ulcer model, circular ulcers deep into the muscle layer appeared in the acetic acid injection area
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic disease involving genes, immunity, diet, environment and other factors. With the change of modern lifestyle, IBD has become more and more common.
How: To remove hair from the back of mice (1.5x1.5cm), take the prepared 1% TNBS solution 150μL and evenly apply it to the hair removal site. Seven days later, the animals were weighed and labeled. After anesthesia, 100 μL 1%TNBS was slowly injected into the rectum of mice using a 1ml syringe through a hose (the length of the hose inserted into the rectum was about 4 cm), and the mice were held upside down for about 1 min, and then the animals were placed back in the cage.
Evaluation: After modeling, the state of the animals was continuously observed, and the modeling status of the animals was determined by DAI score.
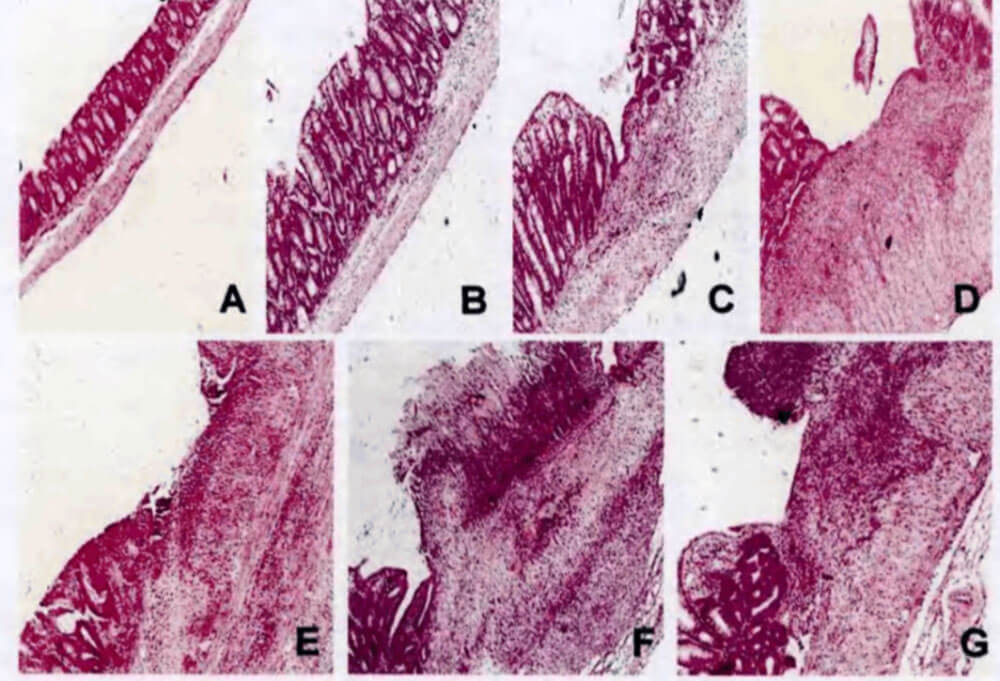
Figure 6 HE staining of colon of model mice (X100)
Minimal change nephrosis (MCN), also known as lipoid nephrosis (lipoid nephrosis), is clinically manifested as nephrotic syndrome: massive proteinuria, hypoproteinemia, edema, hyperlipidemia and so on. MCN is the most common form of glomerular disease in children.
Methods: Male Sprague Dawley rats (body weight 180-220g) were fed with normal diet for 1 week and their urine protein was negative. The model rats were injected with arubicin twice through the tail vein. The first injection was 4mg/kg, followed by another 3mg/kg at 1 week interval. From the first dose, urine was retained for 24 hours at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th weekends, during which a high-protein diet was given. The animals were killed at the end of the fourth week, and blood samples and kidneys were collected for corresponding examination.
Evaluation: Urinary protein, plasma albumin, total protein, serum cholesterol and blood Cr were determined. H&E and PAS staining were performed on pathological sections of kidney. Finally, ultrastructure of kidney was observed by transmission electron microscopy.
Chronicrenal failure (CRF) refers to a decrease in Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) due to severe impairment of nephron and renal function on the basis of various chronic kidney diseases. A syndrome characterized by retention of metabolites in the body, imbalance of water and electrolyte, acid-base balance, and endocrine disorders.
Methods: SD rats, aged 6-8 weeks, were fed adaptively for 1 week and underwent 5/6 nephrectomy.
Evaluation: The contents of serum creatinine Scr, urea nitrogen BUN and urinary creatinine Ucr were detected by biochemical method.
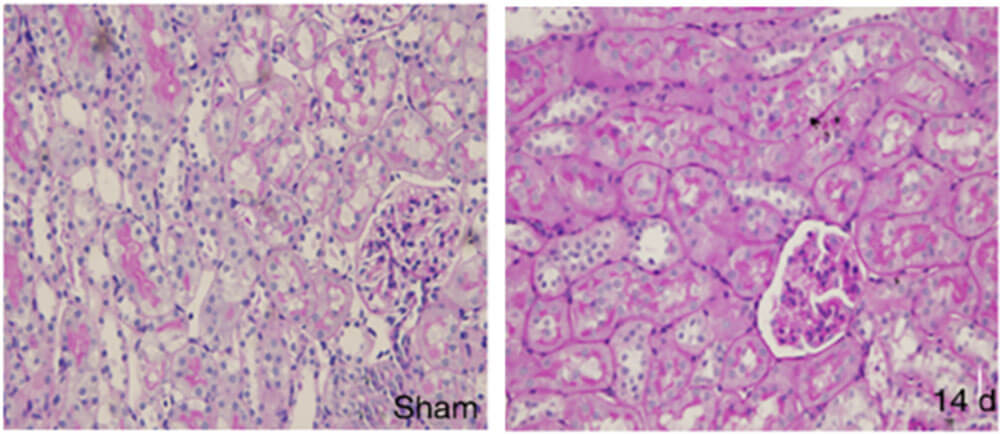
Figure 7 HE staining in sham operation group and model group of chronic renal failure model
Perimenopausal depression refers to the disease that first occurs in perimenopause, with anxiety and depression as the main symptoms.
Methods: SPF grade female C57 mice, weighing 20-25g, were modulated by bilateral ovariectomy
Evaluation: The histomorphologic changes were observed by HE staining
Prostatitis is a common and frequently-occurring disease in men.
Methods: Male SD rats, 12 weeks old, were injected with Escherichia coli in the prostatic urethra of the rats. 4 weeks later, the rats showed chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Evaluation: The histomorphologic changes were observed by HE staining.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints of the limbs.
Methods: SD rats, aged 6-8 weeks, were fed adaptively for 1 week, and the rheumatoid arthritis model was induced by full Freund adjuvant injection in the ankle.
Evaluation: The histomorphologic changes were observed by HE staining.
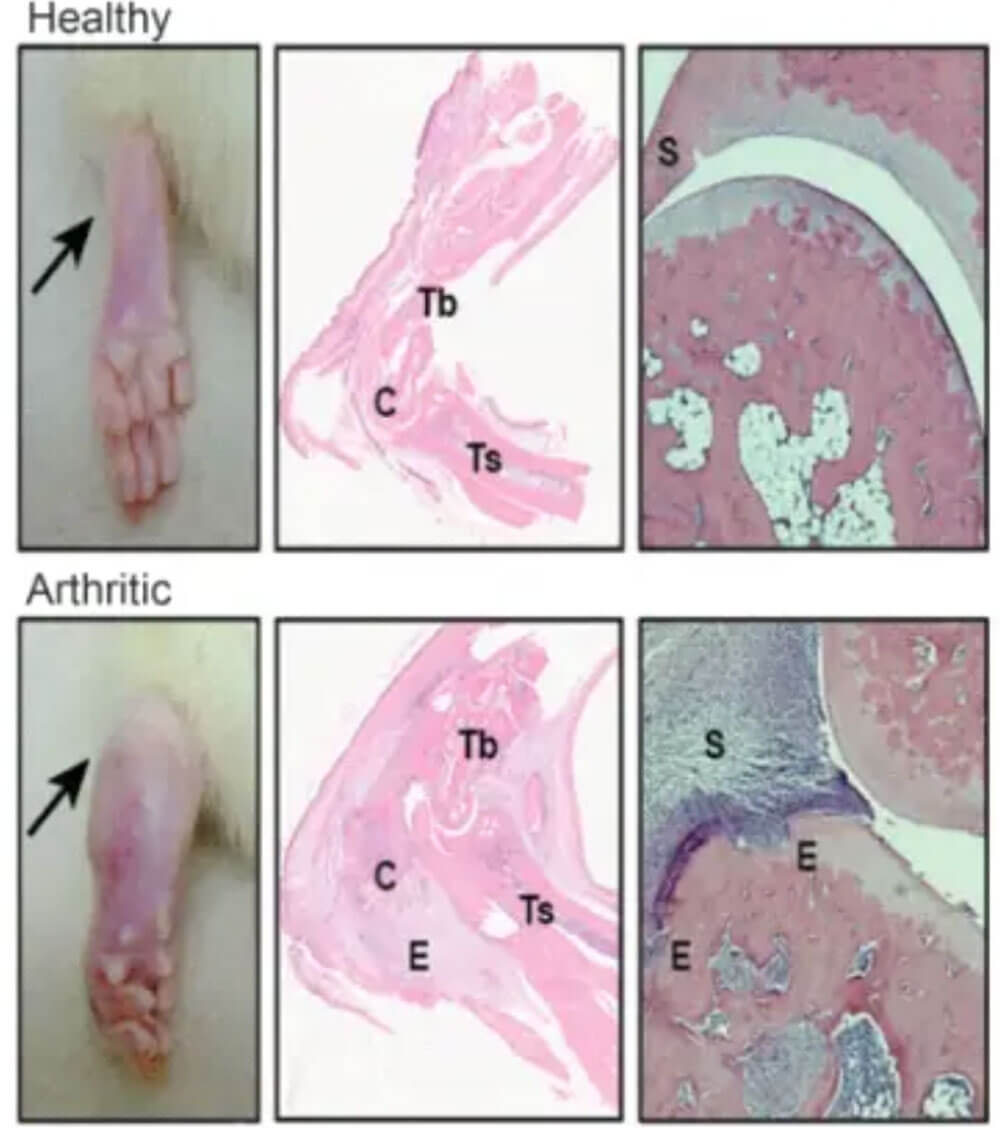
Figure 8 HE staining of rheumatoid arthritis model group and normal group
Hyperthyroidism (hyperthyroidism) is a general term for a group of diseases caused by excessive secretion of thyroxine in the body by a variety of factors, resulting in increased excitability and hypermetabolism of the nervous, circulatory, digestive and other systems.
Methods: Rats were intraperitoneally injected with triiodothyronine (T3) at a dose of 400μg/kg body weight daily for 7 days.
Evaluation: The thyroid weight of model rats decreased significantly, and the iodine content increased significantly.
Acute pharyngitis is an acute inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, submucosa and lymphoid tissue.
Methods: SD rats, weighing 180-220g, were sprayed with ammonia spray twice a day for 3 consecutive days to form acute pharyngitis model
Evaluation: After the successful preparation of the model, the submucosal connective tissue hyperplasia and a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrated the submucosal glands of the pharynx were observed by light microscopy.
viral keratitis (HSK) is the most common form of herpes simplex keratitis. HSK is a kind of blinding eye disease caused by herpes simplex virus infection, which seriously harms the visual function of patients. Its clinical characteristics are mainly manifested as long course and repeated attacks, and eventually lead to corneal leukoplakia, corneal neovascularization, corneal ulcer and even perforation, which seriously harm the visual function of patients.
Methods: Healthy BALB/c mice, both male and female, weight 18-20g, no conjunctivitis, keratitis and other eye diseases in both eyes. Herpes simplex virus type I (HSV-1), with a titer of 2×106pfu/ml before use. Mice were given 2.5g/L chloramphenicol eye drops in both eyes twice a day, and inoculated 1 week later.
Evaluation: After virus inoculation, punctate, dendritic or cartographic lesions appeared in the cornea.
Osteoporosis is a systemic bone disease characterized by decreased bone mass and microstructure of bone tissue.
Methods: Female SD rats aged 3 months were given oral retinoic acid at a dose of 70mg/kg body weight daily for 14 days, and then changed to normal saline for 14 days. Animals are kept regularly, drinking and eating freely.
Evaluation: After oral administration of 3d retinoic acid, the food intake of model rats decreased significantly; On the 14th day, the weight of the animal was significantly reduced, the activity was reduced, and the arched back hair was visible.