- E-mail:bd@braincase.cn
- Tel:+86 18971216876
1. Paraffin section is the most widely used method in routine histology preparation technology. Paraffin sections are not only used to observe the morphological structure of normal cell tissues, but are also the main method used in pathology and forensic medicine to study, observe and judge the morphological changes of cell tissues. They have also been widely used in research in many other disciplines. middle. The paraffin sectioning method includes steps such as material extraction, fixation, washing and dehydration, transparency, wax dipping, embedding, slicing and mounting, dewaxing, staining, dehydration, transparency, and sealing. Generally, it takes several days from tissue extraction and fixation to sealing to make a slide specimen, but the specimen can be stored and used for a long time and is a permanent microscope slide specimen.
2. Frozen section is a method of rapidly cooling the tissue to a certain hardness under low temperature conditions and then slicing it. Because the production process is faster and simpler than paraffin sectioning, it is often used for rapid pathological diagnosis during surgery. There are many types of frozen sectioning, including low-temperature freezer frozen sectioning method, carbon dioxide frozen sectioning method, methanol circulating refrigeration frozen sectioning method, etc. These methods, with the changes of the times and the development of science and technology, were considered very important technologies many years ago and have been gradually eliminated. Of course, some technologies, such as cryostat cryosectioning, are receiving attention.
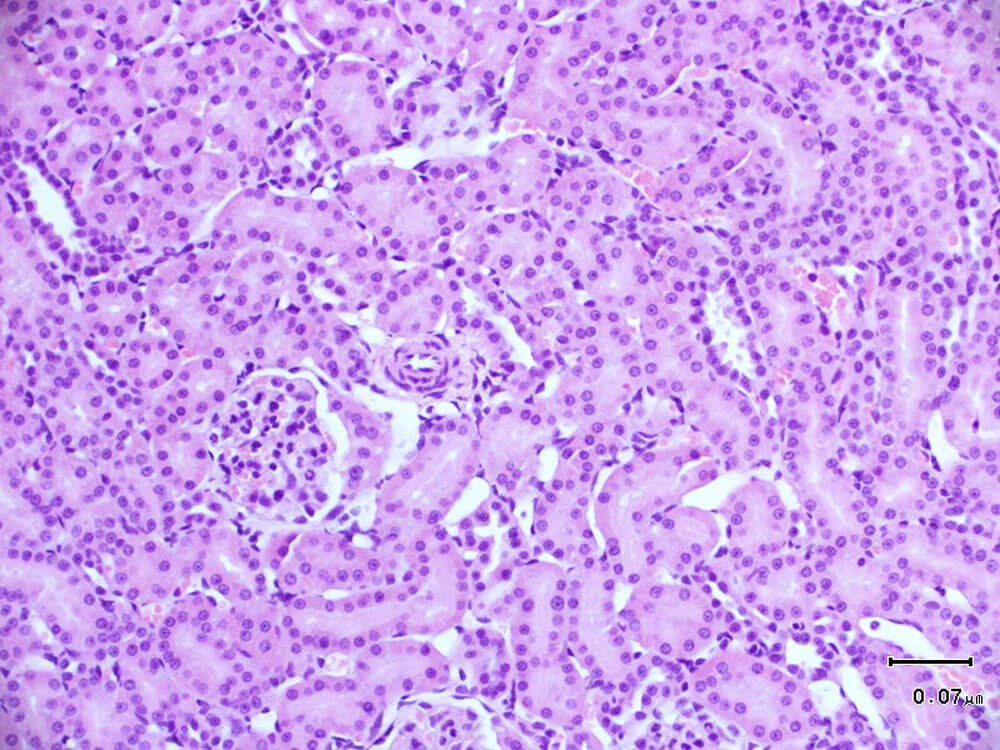
1. HE staining, hematoxylin-eosin staining, referred to as HE staining, is one of the commonly used staining methods in paraffin sectioning technology. Hematoxylin staining solution is alkaline and mainly colors the chromatin in the nucleus and nucleic acids in the cytoplasm purple-blue; eosin is an acidic dye and mainly colors the components in the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix red. HE staining is the most basic and widely used technical method in teaching and scientific research in histology, embryology, and pathology.
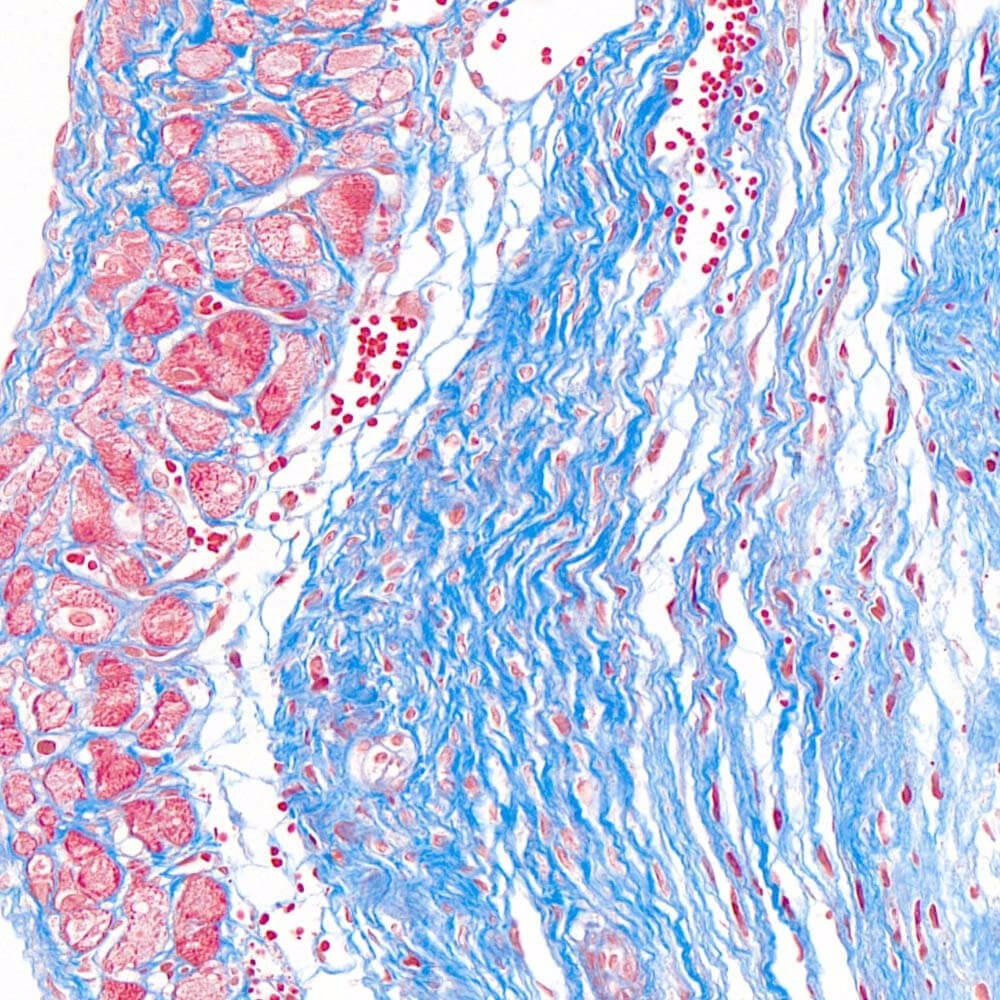
2. Masson staining refers to mixing two or three anionic dyes. Collagen fibers appear blue and muscle fibers appear red. One of the staining methods used to display fibers and inflammatory factors in tissues.
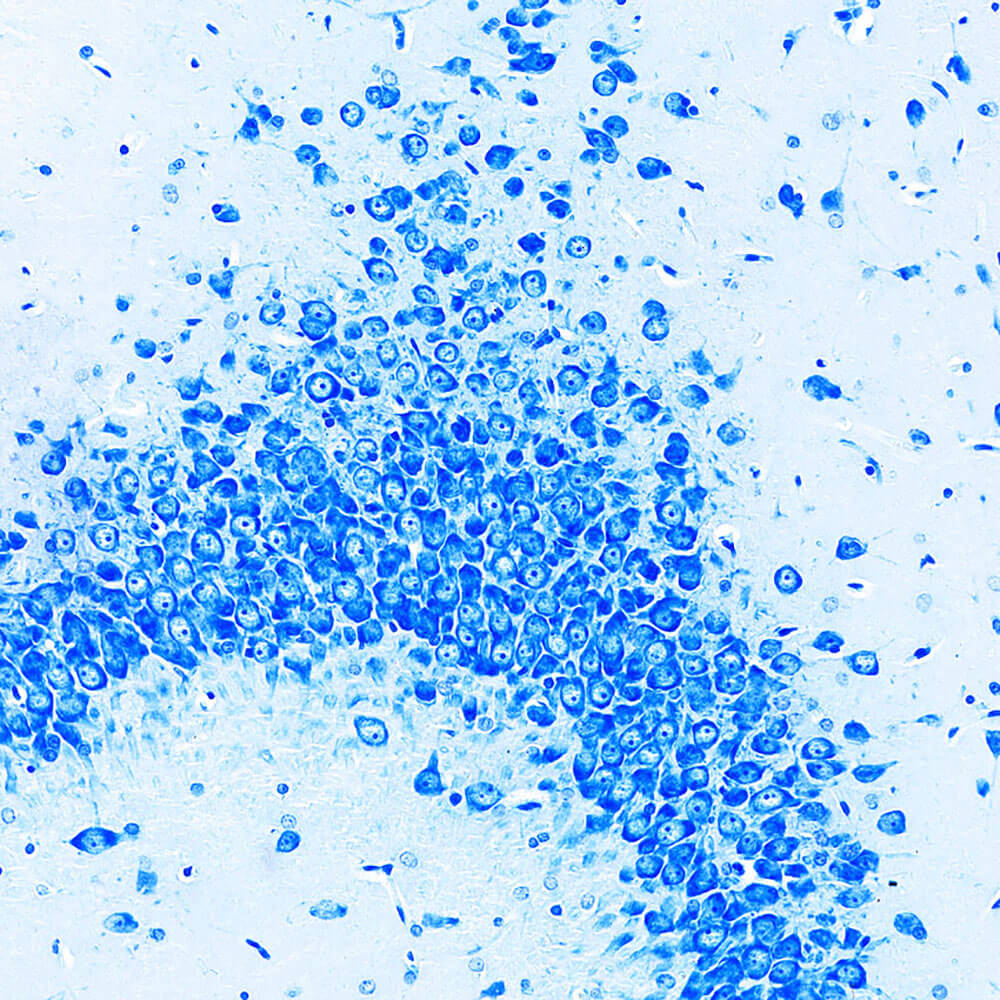
3. Nissl staining is a method of staining nerve tissue with basic dyes. Nissl bodies are a basophilic substance in the cytoplasm and are widely distributed in various neurons. The shape, size and number of Nissl bodies in different neurons vary. Nissl staining can stain Nissl bodies and be used to observe the cell structure within neurons. It can also be used to understand the damage of neurons through the observation of Nissl bodies. Basic dyes used for Nissl staining mainly include tar violet, methylene blue, toluidine blue and thionine.
4. LFB staining. Luxol Fast Blue (LFB) is a copper-phthalocyanine dye that generally stains the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. The myelin sheath is bright blue with a colorless to light blue background. It is mainly used to show the morphological structure and pathological changes of the myelin sheath. The application of LFB myelin staining can well display the myelin structure of neural tissue, which is meaningful for pathological diagnosis and research of neural tissue.
5. Immunofluorescence technology, also known as fluorescent antibody technology, is the earliest developed type of labeled immune technology. It is a technology based on immunology, biochemistry and microscopy. The basic reaction in immunology is the antigen-antibody reaction. Since the antigen-antibody reaction is highly specific, when an antigen-antibody reaction occurs, as long as one of the factors is known, the other factor can be detected. Immunofluorescence technology is to label the antibody (or antigen) with a fluorescent pigment that does not affect the activity of the antigen and antibody. After combining with the corresponding antigen (or antibody), a specific fluorescence reaction will appear under a fluorescence microscope. The main features of this technology are: strong specificity, high sensitivity and fast speed. The main disadvantages are: the problem of non-specific staining has not been completely solved, the objectivity of the result judgment is insufficient, and the technical procedures are still relatively complicated.
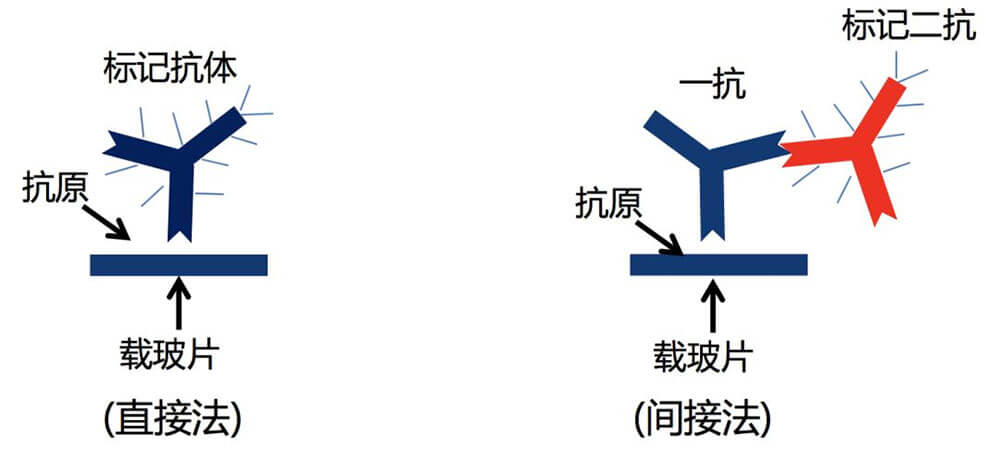
6. Immunohistochemistry is the application of the basic principles of immunology - antigen-antibody reaction, that is, the principle of specific combination of antigen and antibody. The chromogenic reagent (fluorescein, enzyme, metal ion, isotope) labeled with the antibody is colored through a chemical reaction. To determine the antigens (polypeptides and proteins) in tissue cells and conduct localization, qualitative and relative quantitative research on them, it is called immunohistochemistry (immunohistochemistry) or immunocytochemistry (immunocytochemistry). Immunohistochemical techniques can be divided into immunofluorescence, immunoenzyme, immunoferritin, immunogold and radioimmunoassay according to the type of markers.
Slide scanning
Confocal