- E-mail:BD@ebraincase.com
- Tel:+8618971215294
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) belongs to the Parvoviridae family (parvoviridae), a single-stranded DNA virus, and the modified rAAV virus tool has been widely used in gene expression, gene manipulation and gene therapy. It is the simplest type of replication-defective virus found so far, and is dependent on the presence of adenovirus, HSV, and other auxiliary viruses to produce progeny.
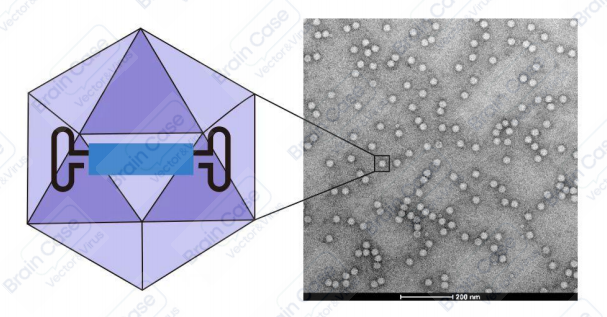
The genome of AAV is a single-stranded DNA molecule ~4.7 kb long. The AAV replicase protein (Rep) and capsid protein (Cap) genes are flanked by inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequences. The virus particle does not have an envelope and is an icosahedron with a diameter of ~20 nm. The rAAV genome only conserves the AAV-derived ITRs, and all viral DNA between the ITRs is replaced by the gene of interest. The AAV ITRs serve as cis-elements, while the AAV Rep, Cap, and helper genes are provided in trans for viral replication and packaging. Therefore, rAAV not only has an excellent safety profile, but also inherits many advantages of wildtype AAV, such as low immunogenicity, multiple serotypes, a wide range of infected host cells, and the ability to mediate the long-term stable expression of foreign genes in vivo.
Table 1 Comparison of several commonly used viral vector tools
|
# |
AAV Vector |
LV Vector |
Retroviral Vector |
Adenovirus Vector |
|
Diamete |
20-30 nm |
90-110 nm |
90-100 nm |
60-90 nm |
|
Copy type |
/ |
/ |
/ |
active |
|
Gene capacity |
2.5 kb |
4 kb |
1.6 kb |
5-6 kb |
|
Integration mechanism |
Directional low frequency |
random high frequency |
random high frequency |
non-integrated |
|
Cell infection |
serotype determination |
Wide range |
split cell |
Wide range |
|
Titer range |
vg/ml |
tu/ml |
tu/ml |
/ml |
|
In vitro infection |
available |
recommended |
available |
available |
|
Immunogenicity |
weak |
normal |
normal |
weak |
|
Positioning injection |
recommended |
available |
recommended |
available |
|
Diffusion ability |
strong |
normal |
normal |
strong |
|
Start time |
2-3 weeks |
3-4 days |
3-4 days |
2-3 days |
|
Duration |
>3 months |
>2 months |
> 2 months |
< 10 days |
In the wide application in neuroscience, rAAVs are increasingly useful tools. Different AAV serotypes exhibit different tropisms and can transduce neural cells in vivo and in vitro. In studies of the structure and function of neural circuits, most AAV serotypes generally exhibit excellent neuronal tropism. These include well-known serotypes such as AAV2/2 (also commonly referred to as AAV2), 1, 8, 9, DJ, php.s, and others. Additionally, AAV5 can efficiently target astrocytes, especially when used in conjunction with astrocyte-specific promoters such as GFAP or GfaABC1D. It is worth noting that transduction of microglial cells appears much more challenging. As of now, only capsid-modified AAV6, as well as the AAVMG1.2 series of serotypes screened by the Minmin Luo laboratory at Peking University, have been shown to enhance the transduction ability of microglial cells. Host cells infected with rAAVs are unable to produce new viral particles, rAAVs cannot efficiently transmit trans-synaptically between neurons. The anterograde, retrograde, and bidirectional transport properties of AAVs are serotype- and concentration-dependent. Therefore, it is very important for researchers to select the appropriate serotype of AAV. In general, most AAV serotypes prefer to enter the cell bodies of neurons at the injection site, and subsequent cellular trafficking may result in the spread of transgenic products throughout the whole neuron. This property may be useful for labeling neuronal projections and manipulating projection targets.
Table 2 Tissue infection tropism of different serotypes of rAAV
| Serotype | Application description |
|---|---|
| AAV/PHP.B | CNS, with higher infection efficiency in neurons and neuroglia, about 40 times that of type 9, can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and placental barrier. |
| AAV/PHP.S | PNS, capable of infecting peripheral neurons, can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and placental barrier. |
| AAV/PHP.eB | CNS, based on PHP:B enhanced version, more suitable for the central nervous system, can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and placental barrier. |
| AAV/B10 | CNS, suitable for the central nervous system, can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, and does not accumulate in the liver. |
| AAV/B22 | CNS, suitable for the central nervous system, can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, and does not accumulate in the liver. |
| AAV/5 | The extracellular adhesion molecule is N-sialic acid, suitable for lungs, eyes, nerves, etc. Muscles, liver, retina, central nervous system. |
| AAV/7 | Suitable for muscles, liver, retina, and the central nervous system. |
| AAV/8 | Suitable for the liver, eyes, central nervous system, muscles, with the receptor being LamR. |
| AAV/9 | The broadest spectrum serum type. Good systemic infection rate, can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, placental barrier. In neural circuit research, it can be used as a retrograde tracer, non-synaptic marker for anterograde tracing. |
| AAV/DJ | Suitable for in vitro experiments, cell infection. |
| AAV/DJ-8 | Based on AAV/DJ enhanced version |
| AAV/DJ-9 | Fast retrograde tracing non-synaptic markers in avian neural circuits. |
| AAV/MG1.2 | Efficient transfection of small glial cells, suitable for in vivo experiments. |
| AAV/CMG | Efficient transfection of small glial cells, suitable for in vitro experiments. |
| AAV/13 | Suitable for precise in situ labeling within brain parenchyma. |
| AAV/Retro | In neural circuit research, it can be used as a retrograde tracer, non-synaptic marker |
| AAV/11 | Compared to AAV/Retro, AAV/11 improves distribution characteristics and retrograde transport efficiency. It can also efficiently infect glial cells. |
| AAV/BR1 | Targets endothelial cells in the brain vasculature (good effect on capillaries, moderate effect on arterioles and venules, poor effect on retina and vitreous). |
| AAV/BI30 | Targets endothelial cells in the brain vasculature. |
| AAV/MaCPNS1 | Effective transduction of the peripheral nervous system, capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier and infecting the central nervous system in macaques and rhesus monkeys. |
| AAV/olig001 | Targets oligodendrocytes, with relatively low targeting to peripheral organs, especially the liver. |
| AAV/1 | Suitable for muscles, heart, skeletal muscles (including cardiac muscles), and neural tissues. |
| AAV/Mac | In neural circuit studies, high titers can be used as serotypes for anterograde transsynaptic tracing. |
| AAV/Anc80L65 | Effectively transduces the central nervous system of non-human primates, capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier (via intravenous injection). |
| AAV/6 | Effective transduction of mammalian inner ear cells in the auditory system; suitable for infecting blood cells, such as T cells. |
| AAV/2 | The extracellular adsorption molecule is heparan sulfate proteoglycan, suitable for research in ophthalmology and central nervous system, among other areas. |
| AAV/6m | Specifically targets astrocytes. |
| AAV/Pan | Pancreas (via intraperitoneal injection). |
| AAV/rh10 | Central nervous system (can transduce neurons in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia in mice), retina, smooth muscles, lungs, liver, heart, pancreas, and kidneys. |
| AAV/7m8 | Retinal cells (injection into the vitreous chamber). |
| AAV/MacPNS2 | Effectively transduces the peripheral nervous system, capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier and infecting the central nervous system in macaques and rhesus monkeys. |
| AAV/CPP1.6 | Efficiently penetrates the blood-brain barrier in rodents and non-human primates. |
| AAV/Ark313 | Efficiently transduces T cells in mammals. |
Brain Case offers a variety of promoters for selection, which, when combined with different serotypes of AAV, can enhance the specificity of expression of the gene of interest in targeted tissues and cells. Promoters are DNA sequences that control gene transcription and can activate gene expression under specific conditions, selecting and screening appropriate promoter region is a key factor in achieving virus-specific expression. Typically, gene expression is influenced by cis-acting elements and trans-acting factors transcription factors. For example, enhancers of some genes are located far upstream or even downstream of the gene, so selecting and screening appropriate promoters for virus vectors is a crucial step. By selecting the appropriate promoter and AAV serotype, it is possible to increase the targeted expression of the gene of interest in specific tissues and cells, allowing for more precise gene regulation and therapeutic applications.
Table 3 AAV Vector Production: list of promoters targeting different organs and cells(Partial)
| Promoter | Description | Cell tropism | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMV | Human cytomegalovirus immediate early enhancer/promoter | —— | —— |
| CAG | CMV early enhancer fused to modified chicken β-actin promoter | —— | —— |
| EF1α | Human eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 α1 promoter | —— | Human |
| nEF1α | Human eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 α1 short form | —— | Human |
| UbC | Human ubiquitin C promoter | —— | Human |
| U6 | U6 promoter | —— | —— |
| hSyn | Human synapsin I promoter | Mature neurons | Human |
| CaMKIIα | Mouse α-calcium-calmodulin dependent kinase II promoter | Pyramidal neurons | Mouse |
| GfaABC1D | Human glial fibrillary acidic protein promoter | Astrocytes | Human |
| GFAP | Human glial fibrillary acidic protein promoter | Astrocytes | Human |
| hCD68 | Homo sapiens CD68 molecule promoter | Microglia | Human |
| ChAT | Choline acetyltransferase promoter | Cholinergic neurons | Mouse |
| rGAD67 | Rat glutamate decarboxylase 1 promoter | GABAergic neurons | Rat |
| mGad65 | Mouse glutamic acid decarboxylase 2 promoter | GABAergic neurons | Mouse |
| mDlx | Mouse distal-less homeobox 5 and 6 promoter | GABAergic neurons | Mouse |
| fSST | Takifugu rubripes (fugu) somatostatin promoter | GABAergic neurons | Takifugu rubripes (fugu) |
| S5E2 | The E2 regulatory element promoter | PV cortical interneurons | Mouse |
| mOXT | Mouse neuropeptide oxytocin promoter | Oxytocin (OT) neurons | Mouse |
| mOXTR | Oxytocin receptor promoter | Oxytocin (OT) neurons | Microtus ochrogaster |
| Tph2 | Tryptophan hydroxylase 2 promoter | Serotonergic neurons | Rat |
| D1 | D1 dopamine receptor promoter | Dopaminergic neurons | Mouse |
| mTH | Mouse tyrosine hydroxylase promoter | Dopaminergic neurons | Mouse |
| L7-6(Pcp2) | The Purkinje cell protein 2 (PCP2)/L7 promoter(henceforth L7) | Purkinje cell neurons | Mouse |
| PRSx8 | The Phox2b-activated artificial promoter | Phox2 (including catecholamine) neurons | Human |
| TRPV1 | Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 promoter | Pain-related neurons | Mouse |
| MeCP2 | Methyl CpG binding protein 2 promoter | Rett syndrome related neurons | Mouse |
| TRE-tight | Tetracycline-responsive element promoter | —— | —— |
| cFos | Immediate early gene C-fos promoter | —— | Mouse |
| cTNT | Chicken cardiac troponin T promoter | Cardiomyocytes | Chicken |
| TBG | Human thyroxine-binding globulin promoter | Hepatocytes | Human |
| LP1B | Liver specific promoter | Liver cells | Human |
| hAAT(HCR+hAAT) | Hepatic locus control region (HCR) of ApoE enhancer +human α1-antitrypsin promoter | Liver cells | Human |
| mTIE1 | Mouse tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-like and EGF-like domains 1 promoter | Endothelial cells | Mouse |
| TUBA1A(Tα1) | Tubulin alpha promoter | Early neurons | Rat |
| hNPPC | Human c-type natruiretic peptide precursor promoter | Oligodendrocytes/Schwann cells | Human |
| fPV | Parvalbumin promoter | GABAergic neurons | Takifugu rubripes (fugu) |
| fNPY | Neuropeptide Y promoter | GABAergic neurons | Takifugu rubripes (fugu) |
| MCK | Muscle creatine kinase (MCK) promoter | Muscle cells | Mouse |
| MHCK7 | α-MHC enhancer+MCK7 | Muscle cells | Mouse |
| ICAM2 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 promoter | Endothelial cells | Human |
| rpe65 | Retinal pigment epithelium 65 promoter | Eye cells | Cynops Pyrrhogaster |
| hRK | Rhodopsin kinase promoter | Eye cells | Human |
| Nrl | Neural retina leucine zipper (Nrl) promoter | Eye cells | Mouse |
| Rho | Rhodopsin(Rho) promoter | Eye cells | Bovine |
| hCalb2 | Calretinin promoter | Neurons and cancer cell | Human |
| mAVP | Vasopressin promoter | Magnocellular neurons | Mouse |
| SFFV | Spleen focus‑forming virus | Immune cell | Mouse |
Clinically, AAV programs have largely focused on degenerative retinal disorders, which are most efficiently targeted to the outer retina via subretinal injection and the inner retina and other cell types flanking the vitreous via intravitreal injection. In the only cochlear gene transfer study to date that has been performed in humans, human adenoviral vector was injected via an oval window procedure. AAV intraparenchymal injections have proven successful in numerous pre-clinical studies using mouse models of lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and Huntington’s disease (HD). For motor neuron disorders, multilevel injections into the spinal cord parenchyma have been successful in delivering therapeutic agents in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) mouse models. While this therapy poses significant risks and challenges in large mammals or humans, some teams have made significant progress in this approach.
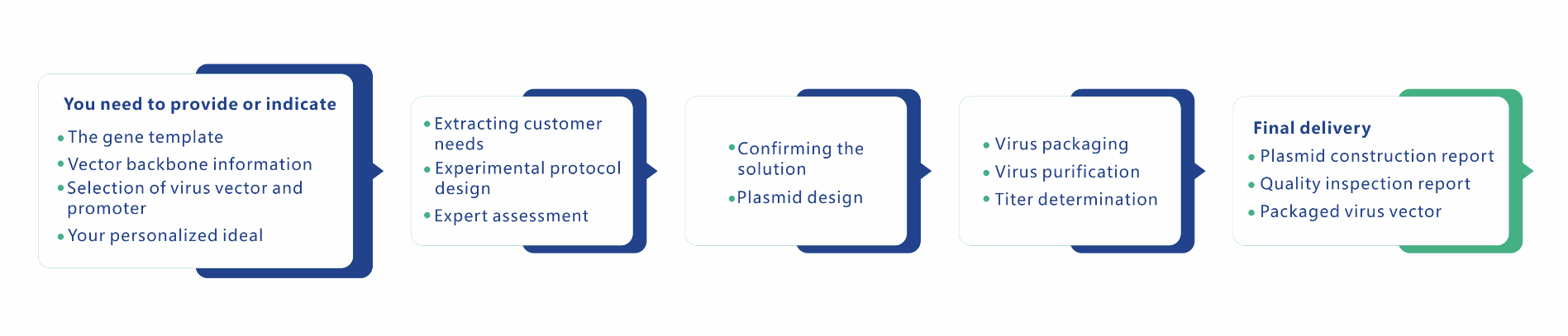
Brain Case specializes in designing and constructing AAV vectors for interfering with or expressing exogenous genes, with applications including overexpression of target genes, CRISPR-mediated gene editing, shRNA-mediated gene interference, and utilizing AAV to deliver the gene backbone of your interest, thereby achieving gene regulation.
Please provide the gene template, vector backbone information, indicate which AAV serotype you will use or your personalized ideal design so that we can communicate and finalize the construction plan with you.