- E-mail:BD@ebraincase.com
- Tel:+8618971215294
In recent years, T cells engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) have been transformative in the treatment of hematological malignancies. During the construction of CAR-T cells, the most common recombinant gene delivery vectors are replication-deficient retroviruses, such as γ-retroviruses (gRVs) or lentiviruses, but these two types of viral vectors will be randomly integrated into In the cell genome, it leads to functional heterogeneity of T cells, transferred gene silencing, and may even activate cell canceration, which limits the effectiveness and safety of cell therapy products.
Gene editing technology has enabled precise integration of transgenes in primary human T cells, which has broadened the scope of engineered T cells in basic research and clinical settings. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is the most widely used in vivo gene therapy delivery vector. It is usually not integrated into the host genome and has high efficiency and low toxicity. Therefore, it can be used as a safer delivery vector for T cell genetic engineering. However, to date, no AAV serotype has been able to efficiently transduce mouse T cells.
On January 12, 2023, Justin Eyquem's team at the University of California, San Francisco, and Asokan's team at Duke University School of Medicine published the article An evolved AAV variant enables efficient genetic engineering of murine T cells in the journal Cell.

This study used saturation mutations on AAV6 to screen an AAV variant, Ark313, that efficiently transduces mouse T cells, and determined through CRISPR genome-wide screening that QA2 is an important factor in efficient transduction of Ark313. Ark313 can be used for nucleoside-free transfection DNA delivery, CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout, and targeted integration of large transgenes. Ark313 can achieve efficient transgene delivery to mouse T cells and effective and precise targeted integration of large fragments of DNA, and can be used to construct safer and more accurate CAR-T and TCR-T cells. This efficient gene targeting provides new possibilities for improving the efficiency of cell therapy and conducting T cell immunity.
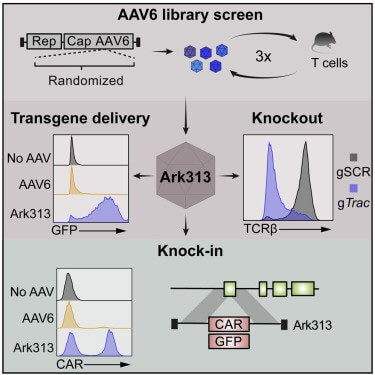
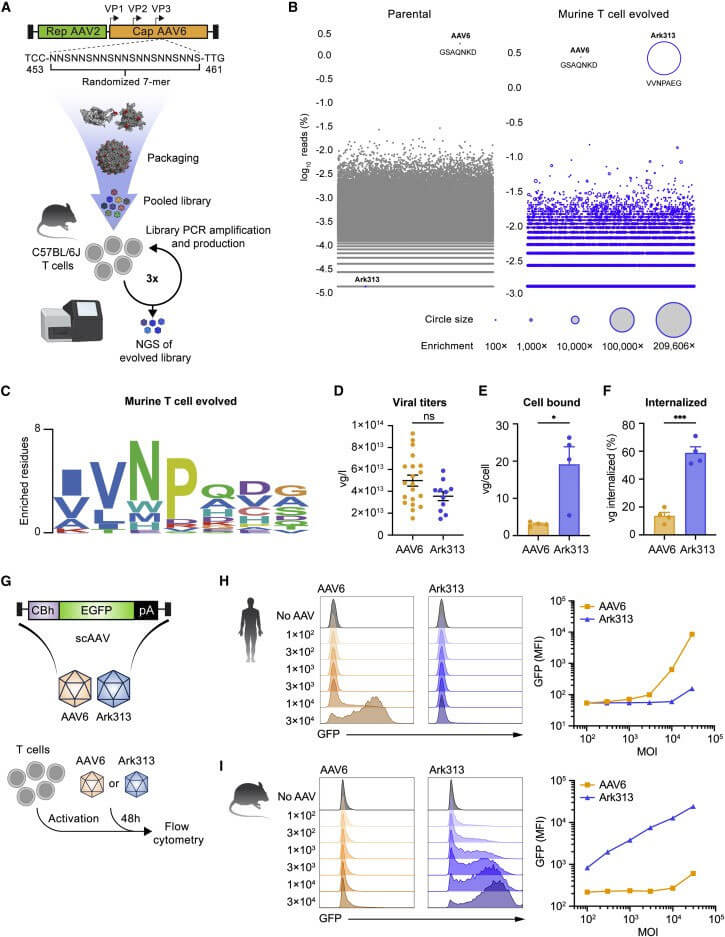
The author first performed saturation-induced mutations on the AAV2/6 genome (AAV2 Rep gene, AAV6 Cap gene). The mutation mainly occurred in the variable region IV (454-460) of the capsid protein VP3 subunit, which is involved in host cell invasion and Neutralizing antibody induction. Primary T cells from C57BL/6J mouse spleen cells were further used to screen the capsid protein library, and the highly targeted mouse T cell serotype Ark313 was obtained. The binding, absorption ratio and transduction efficiency of Ark313 to murine T cells are significantly higher than that of AAV6, which indicates that there are specific host factors in murine T cells that promote the binding and absorption of Ark313. Finally, through CRISPR genome-wide knockout screening, it was determined that mouse QA lymphocyte antigen 2 (QA2) is an essential host factor for Ark313 transduction.
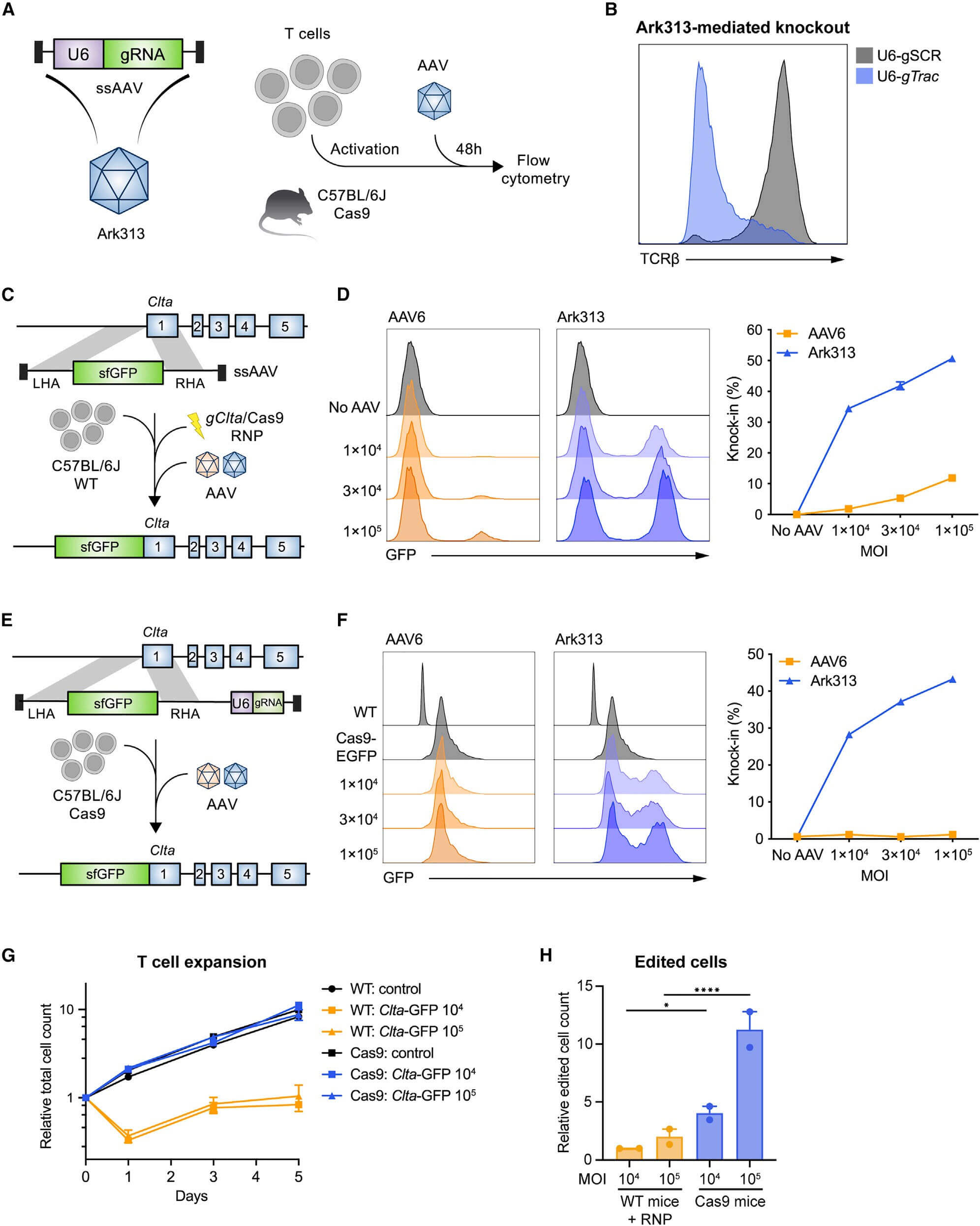
The authors first tested the ability of Ark313 to target Trac to deliver sgRNA expression cassette. The knock-in rate reached 84% by flow cytometry, while non-specific integration mediated by Ark313 is an extremely rare event. Secondly, the ability of Ark313 to deliver large fragments of DNA was evaluated, and it was found that the knock-in efficiency of Ark313 for HDRT (such as GFP expression genes) can reach 30%-50%, which is much higher than that of AAV6. To further reduce cell loss associated with RNP nuclear ligation and increase edited cell yield, expressing sgRNA with HDRT on a single vector resulted in efficient knock-in and low toxicity. These data demonstrate the superior performance of Ark313 in transient gene delivery and targeted integration in primary murine T cells. The high transduction knock-in efficiency of Ark31 co-delivered with HDRT and sgRNA could facilitate the large-scale production of T cells for in vitro and in vivo applications.
Application of Ark313 modified T cells in immune cells
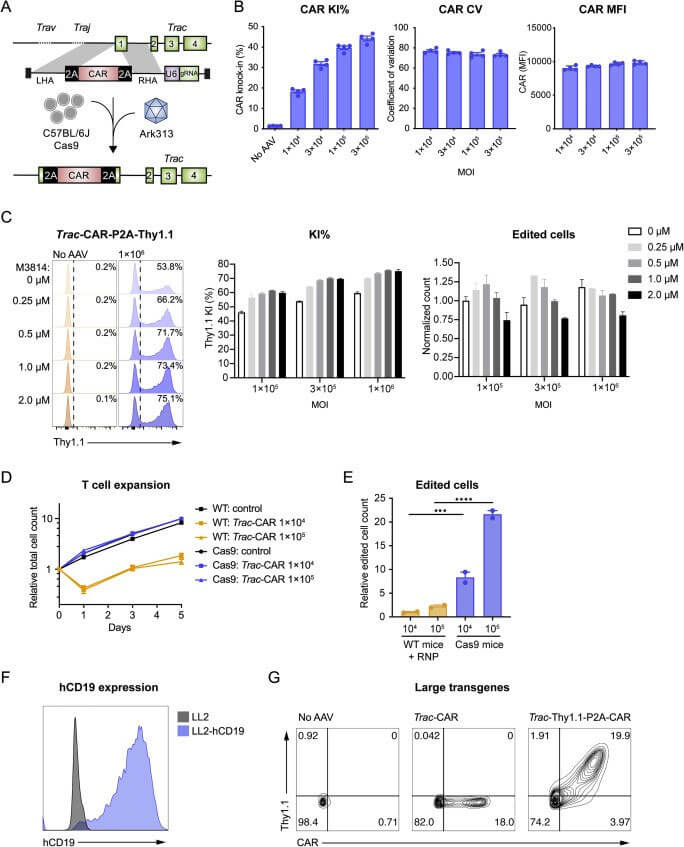
The authors sought to use Ark313 to engineer T cells to study adoptive cell therapy for cancer. First, a HDRT targeting Trac exon 1 is designed to express transgenes under endogenous promoters and integrated receptors relevant to immunotherapy (such as mouse CAR targeting human CD19, hCD19-targeting HIT or Trg OT-I TCR), test results show that the knock-in efficiency of Ark313-mediated CAR can reach 45%. When used in combination with an NHEJ inhibitor (M3814), the knock-in efficiency of Ark313-mediated can reach 75%. In addition, T cells targeting hCD19 exhibited significant cytotoxicity against antigen-expressing cells. When two independent Ark313 vectors were selected to target Clta and Trac genes respectively, more than 8% of cells achieved double knock-in, further highlighting the potential of Ark313 in engineering complex gene-edited T cell therapies.
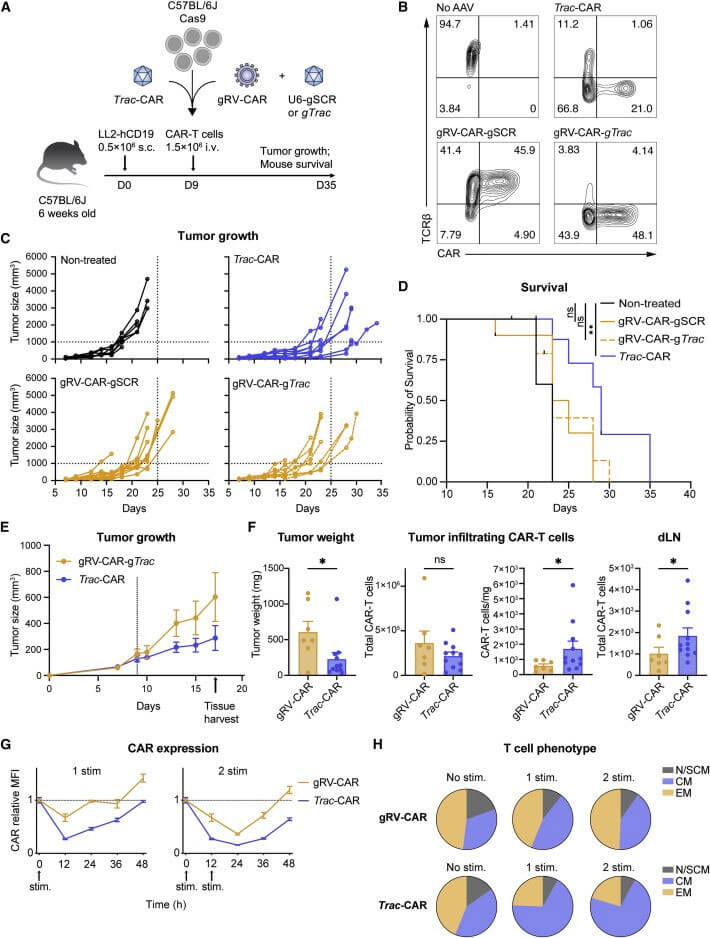
Human TRAC-CAR-T cells outperform retrovirally engineered CAR-T cells in controlling B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) xenograft tumors. To explore whether TRAC-CAR-T cells maintain their superiority in solid tumor models with normal immune function, the authors used Ark313 to construct Trac-CAR-T cells and gRV to construct CAR-T cells, respectively expressing h19m28z. The model was modeled by injecting LL2-hCD19 cells into C57BL/6J mice, and a single dose of CAR-T cells were injected retroorbitally 9 days later. The results showed that gRV-CAR-T cells could not improve the survival rate of mice in vivo, while Trac-CAR -T cells can reduce tumor size and significantly improve survival rates. Like human T cells, the CAR expression of Trac-CAR-T and gRV-CAR-T cells decreased after antigen binding. Trac-CAR-T cells returned to baseline more slowly, and the CAR expression of Trac-CAR-T cells after two stimulations decreased. Recovery expression is faster and the central memory phenotype is elevated following stimulation. These findings demonstrate the efficacy of human TRAC-CAR in mouse solid tumor models and highlight the utility of Ark313 in testing next-generation T cell therapies in immune-competent settings.
In summary, this article discovered the AAV6 variant Ark313, which can efficiently target murine T cells and achieve gene delivery and precise integration of large fragments of DNA. In addition, Ark313 provides great potential for improving T cell therapy, and also for T cells. Immunological research opens new avenues.