Service Workflow
01 Experimental Design
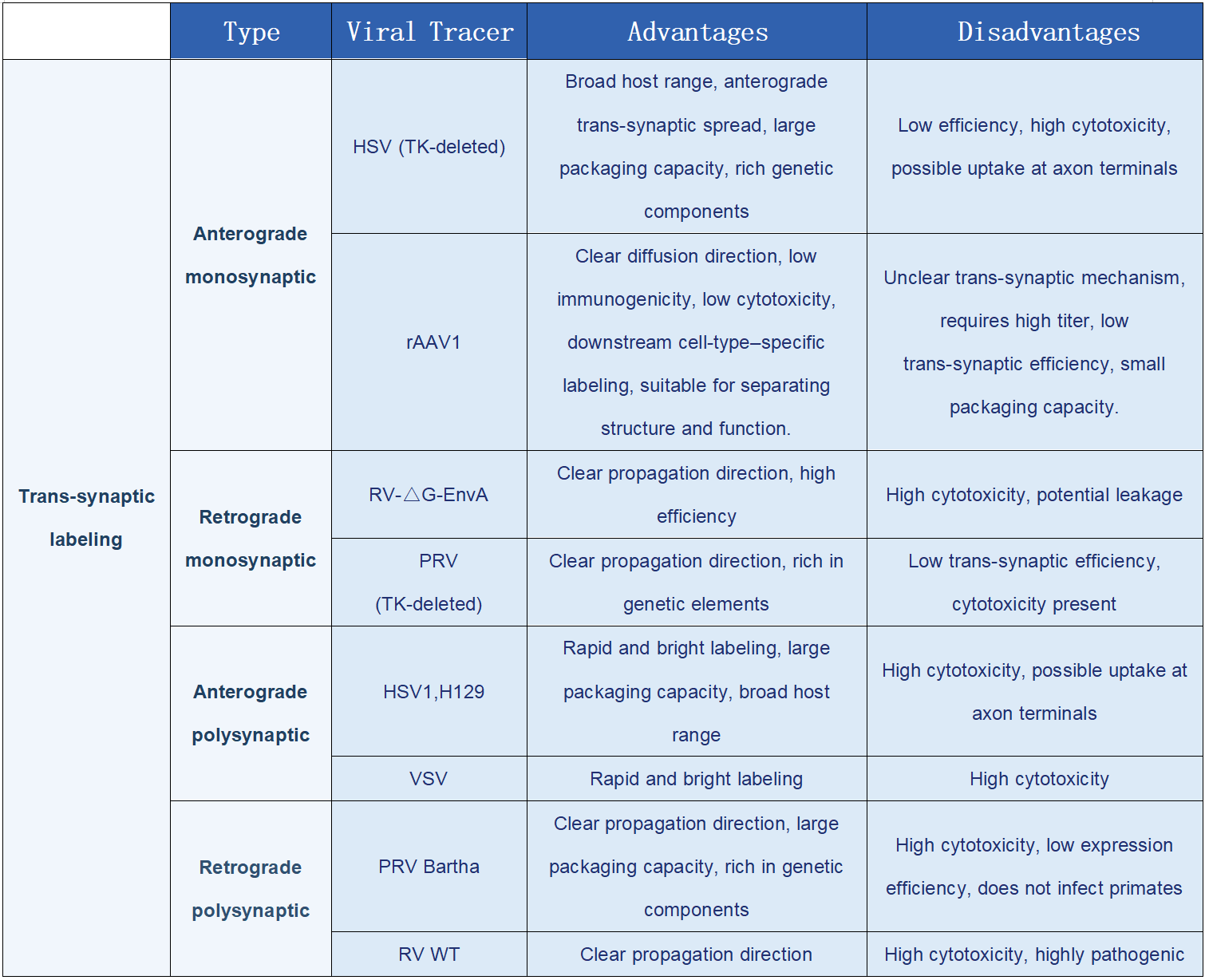
Determine labeling strategies based on research goals (retrograde/anterograde viral tracing, mono-/polysynaptic labeling), select appropriate viral types, and design or select target marker probe panels.
02 Viral Labeling & Tissue Processing
Process samples following the workflow: viral injection → tissue collection → fixation → sucrose dehydration → OCT embedding → cryosectioning.
03 Targeted Spatial Transcriptomics
Perform spatial transcriptomic detection and quantification at the mRNA level.
04 Multidimensional Data Integration & Analysis
Analyze neuronal types, numbers, and spatial distribution labeled by the tracing virus.
Service Advantages
1. High-Specificity Probes and Comprehensive Panel: Precise Neuronal Subtype Identification
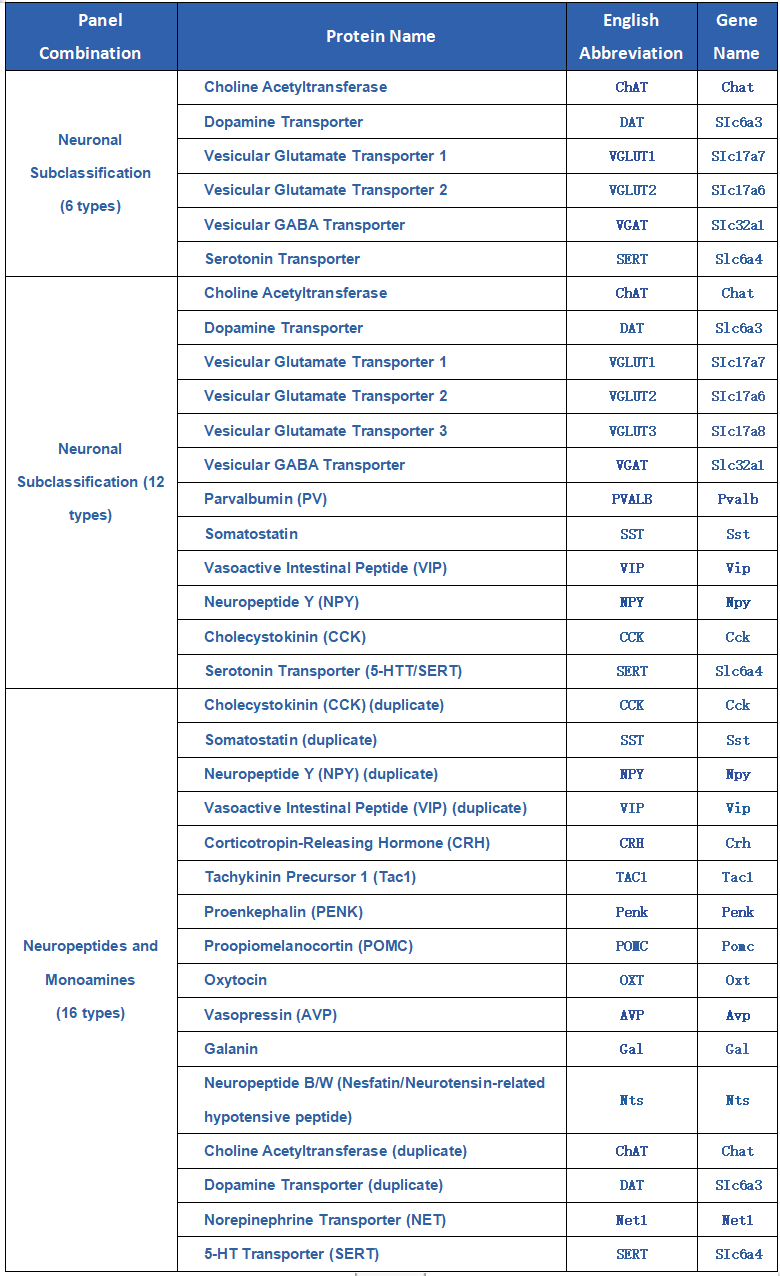
Key neuronal cell types are targeted by selecting hybridization regions with high efficiency and specificity to design dedicated probes. The integrated targeted panel includes over 30 neuronal markers, enabling precise identification of multiple neuronal subtypes. This allows accurate distinction of different neuron types within complex neuronal populations, laying a solid foundation for in-depth studies of neuronal characteristics and functions.
2. The data and results that Brain Case(bd@ebraincase.com) can deliver to you:
A one-stop presentation of research outcomes, including raw images (viral labeling fluorescence images, gene in situ hybridization images), analytical charts (spatial distribution maps of neuronal subtypes, gene expression boxplots/heatmaps), statistical results, and conclusions. All results are delivered in the form of a final report, providing a clear and intuitive display of research findings.
3. Broad Application Prospects:
Applicable across multiple fields of neuroscience research. In developmental neuroscience, it enables tracking of neuronal changes during development; in neurodegenerative disease research, it supports the identification of disease-related neuronal alterations and potential therapeutic targets; in psychiatric disorder studies, it helps uncover abnormalities in brain neural circuits.
Case example below, for reference only
This study investigated the types of neurons in the prelimbic cortex (PrL) of mice that project to the ventral tegmental area (VTA). An RV retrograde trans-synaptic tracing virus was injected into the VTA, and brain slices were collected for in situ hybridization. The detection panel included Choline Acetyltransferase (ChAT), Dopamine Transporter (DAT), Vesicular Glutamate Transporter 1 (Vglut1), Vesicular Glutamate Transporter 2 (Vglut2), Vesicular GABA Transporter (VGAT), and Serotonin Transporter (SERT).
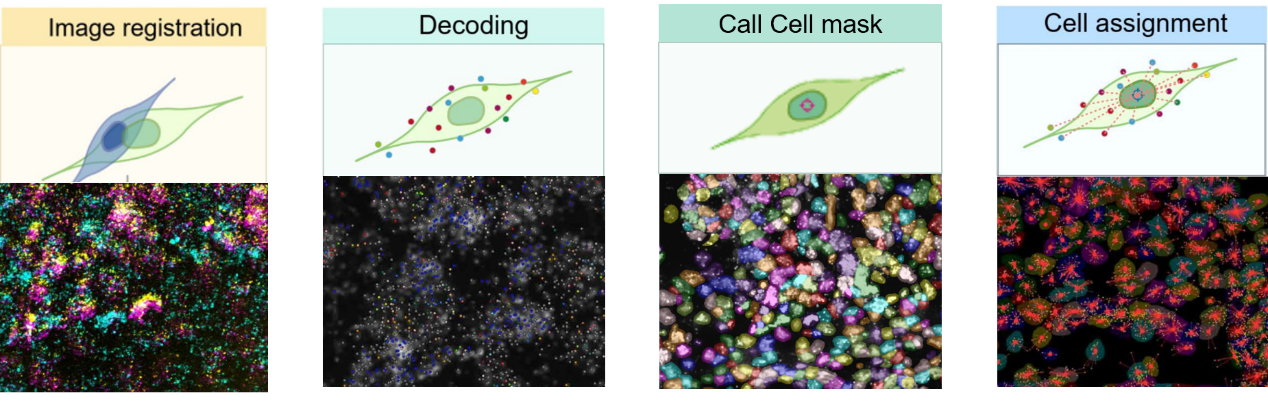
1. Image Calibration
Acquired images were adjusted and optimized to correct for imaging artifacts caused by equipment differences, lighting conditions, or experimental operations, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and reliability.
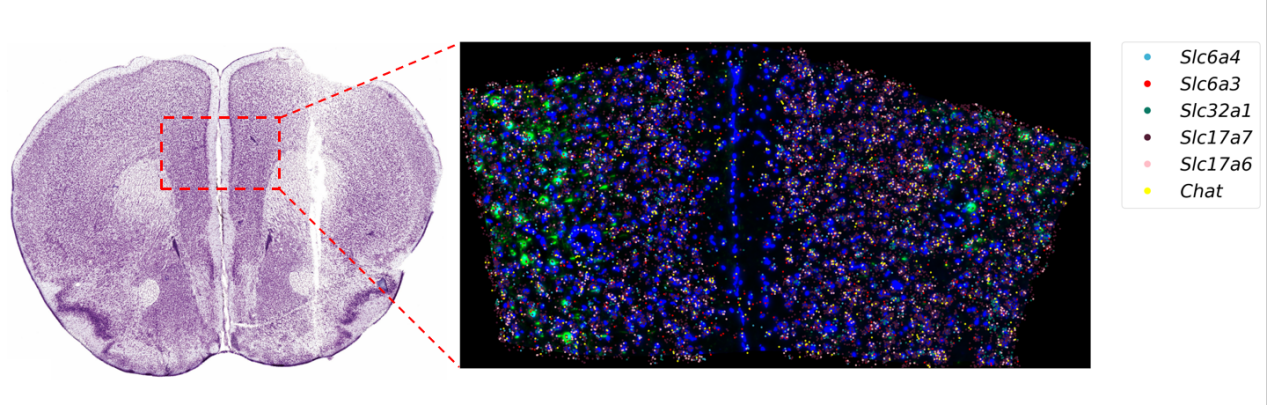 Figure 1: Merged fluorescence image (blue: nuclei, green: virus-labeled cells)
Figure 1: Merged fluorescence image (blue: nuclei, green: virus-labeled cells)
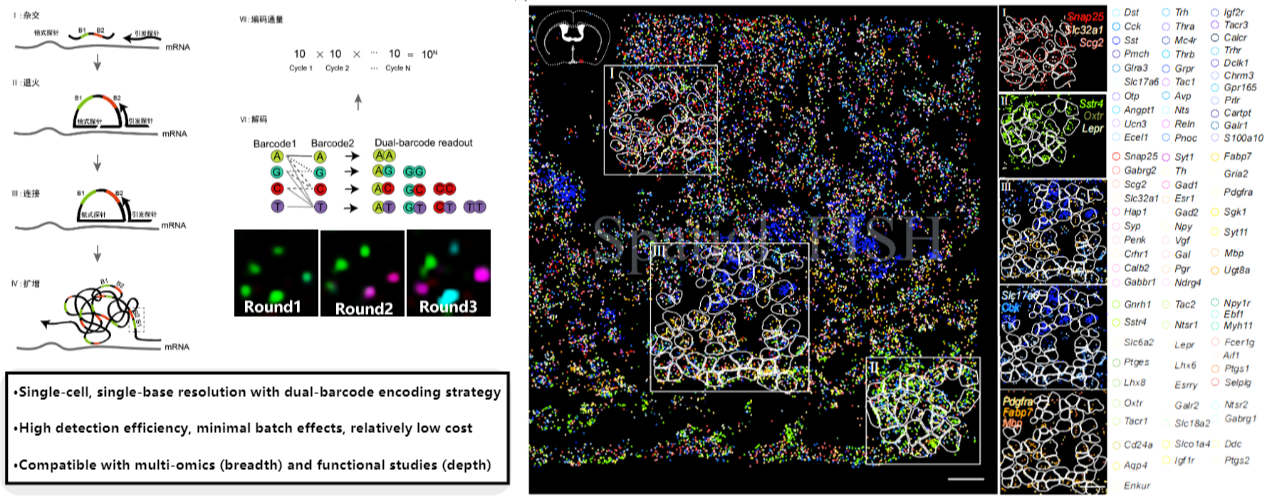
2. Signal Decoding
Fluorescence signals were quantified and spatially localized. Quantification involved measuring signal intensity, area, or other parameters to reflect expression levels, while localization determined the precise spatial position of signals for further spatial distribution and interaction analysis.
 Figure 2: All-gene distribution map (different colored dots represent different gene signals)
Figure 2: All-gene distribution map (different colored dots represent different gene signals)
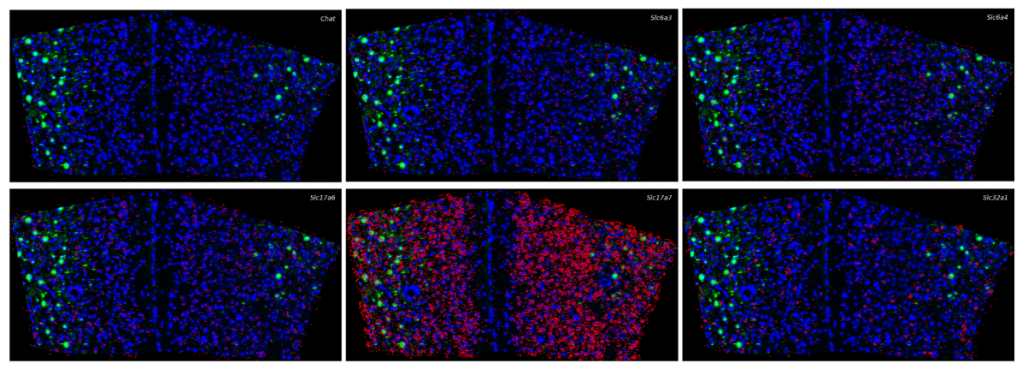 Figure 3: Single-gene distribution map (expression profile of individual gene)
Figure 3: Single-gene distribution map (expression profile of individual gene)
3. Cell Segmentation & Signal Assignment
Image processing was performed to identify and delineate cell boundaries, enabling single-cell localization and segmentation.
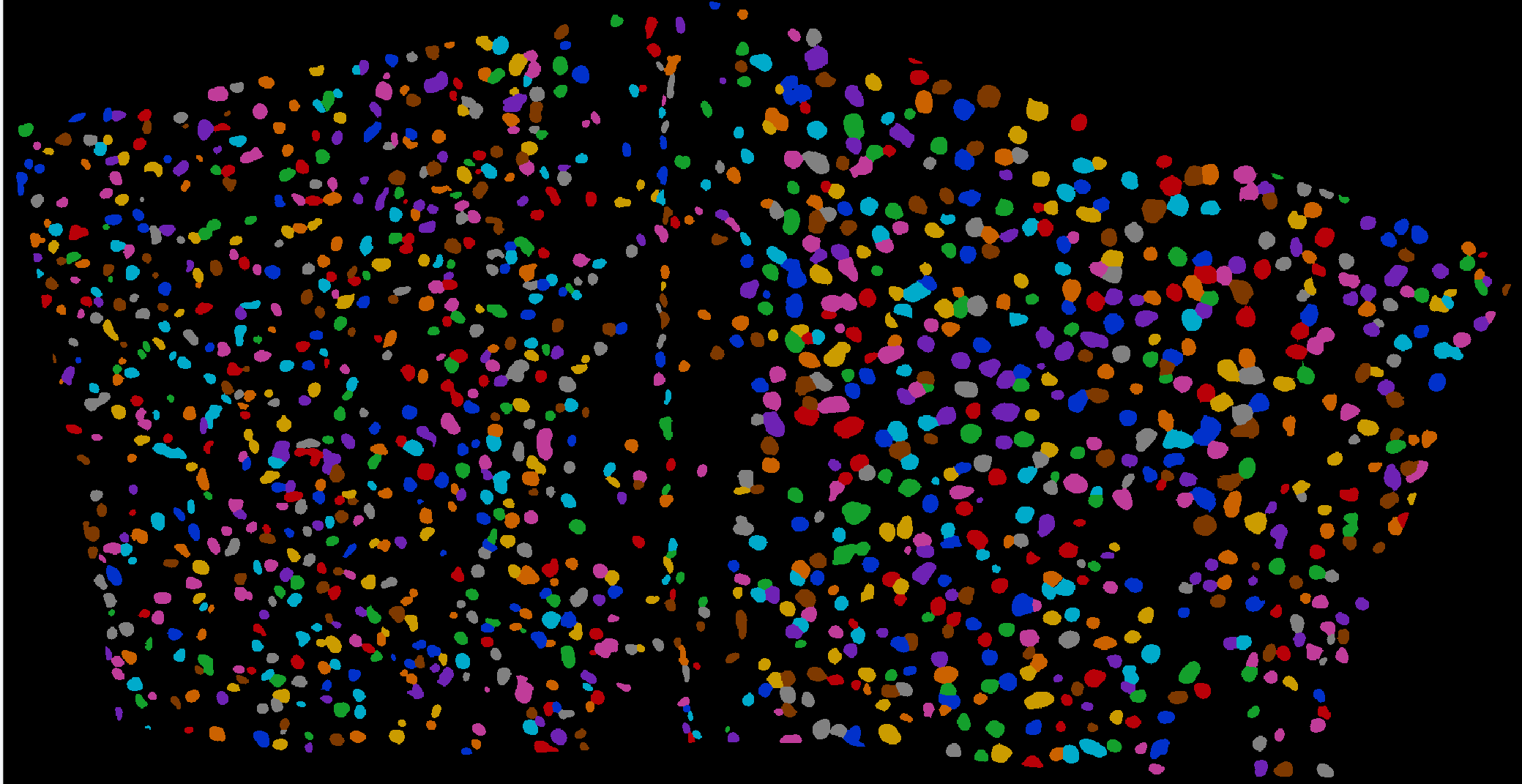
Figure 4: Cell segmentation map (identified cells)
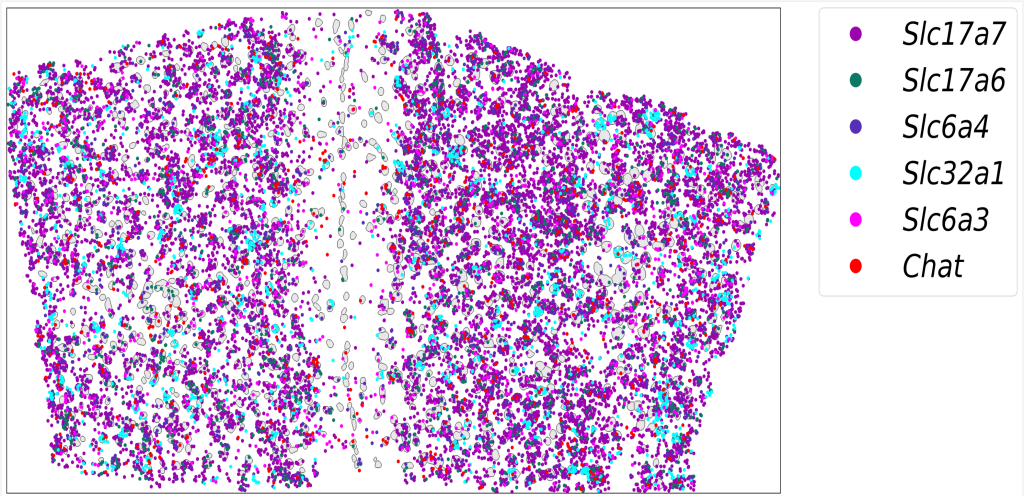
Figure 5: Gene-to-cell distribution map (blue/gray: nuclei; colored dots: different gene signals)
4. Data Statistics
Statistical analysis of the traced virus-labeled cells showed expression patterns for six genes.
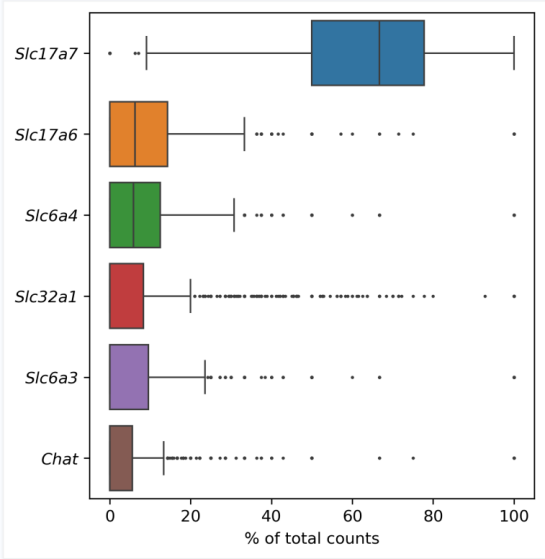
Figure 6: Gene expression boxplots
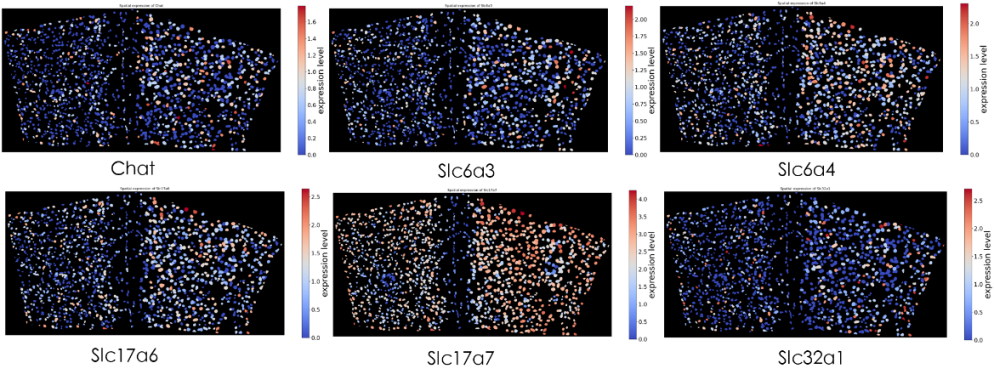
Figure 7: In situ gene expression heatmap
Summary of Results
Among neurons in the prelimbic cortex projecting to the VTA, Sla17a7-expressing cells were the predominant type, accounting for approximately 63% of the population. For inquiries related to neural circuit tracing, spatial omics, or dimensional data analysis and visualization, please contact us at bd@ebraincase.com